Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDrongos deceive but weavers let them
The fork-tailed drongos of Africa manipulate others to get a meal, but there is good reason to let them get away with the deception.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNematode sperm go rogue
Worm sperm a killer when nematode species crossbreed.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePart of brain’s pleasure network curbed in mice with chronic pain
Part of brain’s pleasure network is muffled in mice with chronic paw injuries, a new study finds.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDeepwater Horizon damage footprint larger than thought
In the Gulf of Mexico, most deep-sea corals have escaped damage from the Deepwater Horizon blowout. However, the impact does extend deeper and wider than previously thought.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaurs shrank continually into birds
Steady miniaturization and rapidly changing skeletons transformed massive animals into today’s fliers.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsBirds’ turns match math of quantum matter
Equations that describe superfluidity may explain how information about which way and when to turn spreads in a starling flock.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Octomom’ sets egg-brooding record
The deep ocean reveals a new record as an octopus mom broods the same clutch of eggs for almost 4.5 years.
-
 Life
LifeFor yeast life span, calorie restriction may be a wash
A new technique for growing and tracking yeast cells finds caloric restriction doesn’t lengthen life span, though some researchers question the study method.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStudy linking narcolepsy to autoimmunity retracted
Data linking disorder to immune cells couldn’t be replicated, scientists say.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Oceans
OceansWhales and ships don’t mix well
A 15-year study of blue whales off California has found that major shipping lanes cut through feeding grounds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHippocampus may help homing pigeons explore
When researchers remove pigeons’ hippocampi, birds fly straighter on early parts of journey home.
-
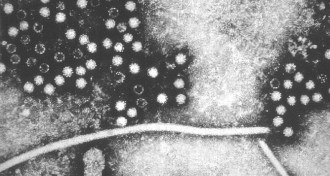 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis E widespread among English blood donors
Screening of 225,000 blood donations reveals a high prevalence of the hepatitis E virus.