Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOctomom and six other extreme animal parents
The octopus that brooded her young for 4.5 years is just the start when it comes to tales of extreme parenting.
-
 Computing
ComputingBarrel jellyfish may hunt with new kind of math
Barrel jellyfish use a new type of mathematical movement pattern to forage for food, a new study suggests.
-
 Life
LifeAirborne transmission of Ebola unlikely, monkey study shows
No evidence found of macaque monkeys passing deadly virus to each other.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDebate rages over mouse studies’ relevance to humans
Last year, researchers said rodents are not good mimics of human inflammation; a new study says the reverse.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyAddiction showcases the brain’s flexibility
People with substance abuse disorders are not just chasing a high. Their brains are adapting to the presence of drug, evidence of humans’ impressive neural plasticity.
-
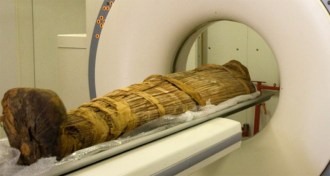 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMummies reveal hardened arteries
Mummy studies suggest heart disease is an ancient malady, not just the product of modern diets and sedentary lifestyles.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDrongos deceive but weavers let them
The fork-tailed drongos of Africa manipulate others to get a meal, but there is good reason to let them get away with the deception.
-
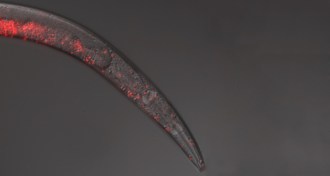 Animals
AnimalsNematode sperm go rogue
Worm sperm a killer when nematode species crossbreed.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePart of brain’s pleasure network curbed in mice with chronic pain
Part of brain’s pleasure network is muffled in mice with chronic paw injuries, a new study finds.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDeepwater Horizon damage footprint larger than thought
In the Gulf of Mexico, most deep-sea corals have escaped damage from the Deepwater Horizon blowout. However, the impact does extend deeper and wider than previously thought.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaurs shrank continually into birds
Steady miniaturization and rapidly changing skeletons transformed massive animals into today’s fliers.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsBirds’ turns match math of quantum matter
Equations that describe superfluidity may explain how information about which way and when to turn spreads in a starling flock.