Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAboriginal lizard hunting boosts kangaroo numbers
An aboriginal technique for hunting lizards with fire in Western Australia feeds wallaroo populations.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProsthesis uses swinging arms to tell legs when to step
Device creates artificial neural connection that could help paralyzed people walk.
-
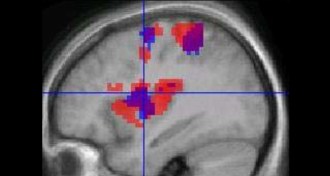 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBusy neurons don’t always draw blood
Study of mice suggests caution in inferring the activity of the brain’s neurons from functional MRI results.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew dolphin species gets a name
A species of humpback dolphin from Australia has now received its proper name.
-
 Life
LifeAnimal source of Ebola outbreak eludes scientists
Researchers are trying to determine whether bats or bush meat transmitted the Ebola virus to people in West Africa.
-
 Life
LifeGrizzly bears master healthy obesity
Tuned insulin signals explain how grizzly bears can fatten up for hibernation in the winter without developing diabetes.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMusic soothes the aging brain in film ‘Alive Inside’
A social worker highlighted in a new documentary goes on a quest to bring tunes to nursing homes.
-

-
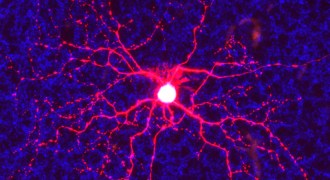 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFor neurons, birthday matters
How brain cells make their connections during development still isn’t well understood. A new study shows that in the eye, a neuron’s birthday makes a difference in how it finds its targets.
-
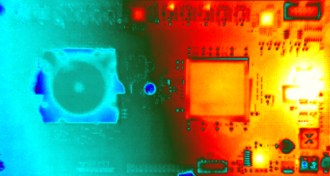 Computing
ComputingBrain-inspired computer chip mimics 1 million neurons
By processing data in parallel, computer chips modeled after the human brain could perform certain tasks, such as pattern recognition, faster and more energy-efficiently than traditional computers.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s your chance to see the last passenger pigeon
On display for the 100th anniversary of her species’ extinction, the final passenger pigeon specimen looks pretty good.
By Susan Milius -
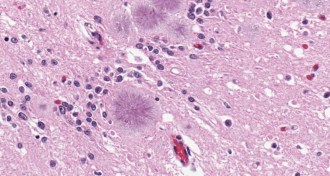 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew tests screen for lethal prion disease
Urine and nasal swabs can detect small amounts of the abnormal prions that cause Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
By Nsikan Akpan