Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsLong before Columbus, seals brought tuberculosis to South America
Evidence from the skeletons of ancient Peruvians shows that seals may have brought tuberculosis across an ocean from Africa.
-
 Life
LifeMalaria parasite’s invasion of blood cells tweezed apart
Tugging on malaria-causing parasite cells with laser optical tweezers suggest that the parasite cells interact only weakly with red blood cells and that the interactions could be disrupted with drugs or antibodies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOlinguito’s bio built by crowd-sourcing
Crowd-sourcing fleshes out the bio of little-known raccoon relative, the olinguito.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsNew subspecies of Philippine tarsier discovered
Genetic tests settle a taxonomic debate surrounding Philippine tarsier, one of the world’s smallest primates.
By Nsikan Akpan -
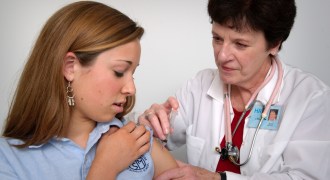 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHPV vaccine protection lasts at least eight years
Immunization shields children from human papillomavirus infection for nearly a decade.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureKiller bug behind coconut plague identified
A pest has devastated coconuts in the Philippines, and scientists now realize the perp is not the bug they thought was causing the damage.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Animals
AnimalsZebra finches go mad with mercury, and other animal updates
Mercury exposure makes zebra finches bold and hyperactive, and additional research from the 2014 Animal Behavior Society Meeting.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDolphins and whales may squeal with pleasure too
Dolphins and whales squeal after a food reward in about the same time it takes for dopamine to be released in the brain.
-
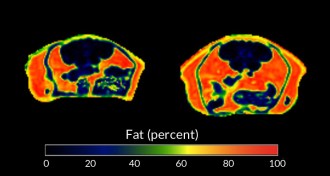 Humans
HumansAntibiotics in infancy may cause obesity in adults
By altering the microbiome of infant mice, drugs predisposed the animals to gain fat as adults.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInflammation-blocking cells might fight often-fatal sepsis
Treatment saved young and old mice from overactive immune response to infection.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Physics
PhysicsCommon motion emerges in swarms of only 10 midges
A swarm of midges may start to fly as a collective group with as few as 10 individuals, a new study shows.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeurons in silk scaffold mimic behaviors of a real brain
Proteins of silkworm cocoons can form the scaffold for a three-dimensional model of a brain.