Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV and illicit drugs are a bad mix. This scientist found an unexpected reason why
The neuroscientist considers themself an outsider, which allows them to embrace people who have been marginalized, including people who have HIV.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists have just turned giant panda skin cells into stem cells
If the pluripotent stem cells can be turned into precursors to egg and sperm cells, the feat could potentially be a big deal for giant panda conservation.
By Jason Bittel -
 Microbes
MicrobesSome bacteria in your mouth can divide into as many as 14 cells at once
The filamentous bacterium Corynebacterium matruchotii has a unique reproductive strategy that might allow it to claim territory quickly.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnts changed the architecture of their nests when exposed to a pathogen
Black garden ants made tweaks to entrances, tunnels and chambers that may help prevent diseases from spreading.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSome healthy fish have bacteria in their brains
Animals including mammals usually protect their brains from infiltrating microbes that can cause disease. But some fish seem to do just fine.
-
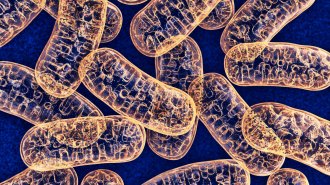 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMitochondria can sneak DNA into the nuclei of brain cells
An analysis of tissue samples from nearly 1,200 older adults found that the more insertions individuals had, the younger they died.
-
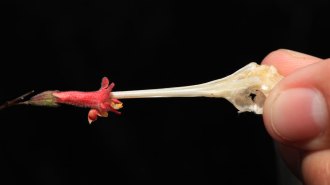 Plants
PlantsProjectile pollen helps this flower edge out reproductive competition
With explosive bursts of pollen, male Hypenea macrantha flowers knock some competitors’ deposits off hummingbird beaks before the birds reach females.
By Nala Rogers -
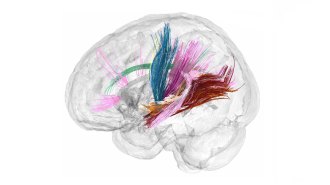 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePregnancy overhauls the brain. Here’s what that looks like
Neuroscientist Liz Chrastil’s brain scans before, during and after pregnancy are providing the first view of a mom-to-be’s structural brain changes.
-
 Life
LifeMega El Niños kicked off the world’s worst mass extinction
Long-lasting, widespread heat and weather extremes may have caused the Great Dying extinction event 252 million years ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient DNA unveils a previously unknown line of Neandertals
DNA from a partial skeleton found in France indicates that European Neandertals consisted of at least two genetically distinct populations.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsBumblebees lose most of their sense of smell after heat waves
A few hours in high temps reduced the ability of antennae to detect flower scents by 80 percent. That could impact the bees’ ability to find food.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentFiddler crabs are migrating north to cooler waters
The crabs are climate migrants and could be a harbinger of changes to come as more species move in.
By Luke Groskin