Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImpotence drug boosts insulin in some with diabetes
A drug called yohimbine lets some people with diabetes secrete more insulin by stopping pancreas cells from binding adrenaline molecules.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsYeast smell underpins partnership with fruit flies
Yeast make fruity aromas that draw flies, which disperse the fungi. Researchers reveal the gene that underpins the mutually beneficial relationship.
-
 Animals
AnimalsRattlesnakes tutor robot on dune climbing
Snakes sidewinding up sand inspire design improvements for robots navigating treacherous slopes.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesGut bacteria protein linked to anorexia and bulimia
Gut bacteria may play a role in eating disorders, a new study suggests.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryMicroscopy providing ‘window into the cell’ wins chemistry Nobel
Three scientists use fluorescence and lasers to see single molecules and other tiny objects.
By Beth Mole and Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsZebra finches use camouflage
In an experiment, zebra finches camouflaged their nests to match the background, even though they lived in captivity and there was no danger of predators.
-
 Paleontology
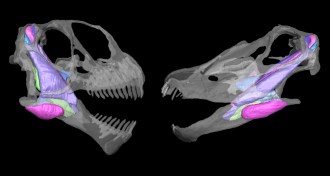
PaleontologyPlant-eating dinosaurs coexisted by munching different vegetation
Differences in skulls allowed sauropods to coexist in an arid landscape by enabling the dinosaurs to tackle different plants.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMelatonin and the watery beginnings of sleep
The tiny zooplankton Platynereis dumerilii use melatonin just as much as we do, suggesting that the origins of sleeplike behavior may lie under the sea.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists garner Nobel for discovering brain’s ‘inner GPS’
Three researchers who found brain cells that allow rats to orient themselves in space have won the 2014 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Planet of the Bugs’ reveals the secrets to insects’ success
Entomologist Scott Richard Shaw explores the evolution of insects and how they came to rule the world.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
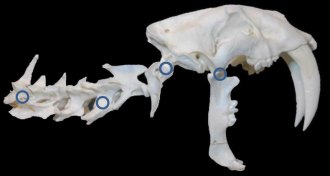
AnimalsHow a saber-toothed cat is like a can opener
A researcher argues that the saber-toothed cat’s teeth acted like an old-fashioned can opener.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s map cells win three scientists Nobel Prize
The discovery of brain cells that provide a sort of “inner GPS” has been awarded the 2014 Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine.