Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCamels’ number of humps may affect their fat storage
The number of humps camels and alpacas have may play a role in how well they store and break down fat.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene variant helps dog evade muscular dystrophy
A dog that has a mutation causing muscular dystrophy has another genetic variant that appears to counteract the disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCamouflaged fish found hiding in plain sight
Rockpool gobies change color depending on their background.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFeedback
Readers discuss methods to prevent sepsis and whether genes are thrifty, while Tina Saey clears up some confusion regarding Ebola's airborne status.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes can redeem themselves to fight disease
With some genetic engineering, bacteria can morph from bad to good and help attack invading cancer cells.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Animals
AnimalsHearing awful or great singing changes birds’ choice
A male bird’s serenade inspires reactions that depend on the quality of songs a female has been listening to.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJet lag affects gut microbes
Jet-lagged bacteria in the gut impair mice’s metabolism, causing obesity and diabetes-related problems.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFrench flamingos froze to death without freezing
Cold snaps in 1985 and 2012 starved flamingos by the thousands in southern France.
-
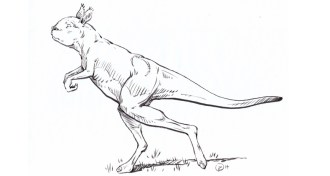 Paleontology
PaleontologyExtinct giant kangaroos tiptoed one leg at a time
Stiff spines, flared hips and other fossil clues suggest extinct, refrigerator-sized kangaroos stepped one hind leg at a time instead of hopping.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsA stressful youth makes for a devoted finch dad
Stress is generally thought to be a bad thing. But a new study shows that under certain conditions, a stressful childhood could make a zebra finch a better father.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHouse fly’s genome hints at detox genes
The house fly's DNA instructions include extra genes that may help detoxify and decompose animal waste.
-
 Animals
AnimalsQuick-moving toads take the straight and narrow path
Cane toads at the front line of an invasion in Australia have evolved to move in straighter paths than those left behind.