Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBirds large and small hop over obstacles in similar ways
Bipedal birds, from tiny quail to huge ostriches, tackled a step in a similar way, minimizing energy cost and maximizing safety.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew frog species discovered in New York City
A new frog species lives up and down the East Coast. It was discovered when ecologists realized its ‘ribbit’ was distinct from the calls of a lookalike species.
-
 Life
LifeA little good news for giant tortoises in the Galapagos
The giant tortoise population on the Galapagos island of Española is on the rebound, but there are still concerns about other markers of conserving the endangered species.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesFrozen caribou feces offers look at virus evolution
Genetic material extracted from caribou poop gives hints about how viruses evolve.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain difference found in people with chronic fatigue
Abnormality found in the brains of a small number of people with chronic fatigue syndrome is intriguing, but needs to be confirmed with more patients.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient jellyfish suffered strange, sandy death
A fossil hints at the unusual series of events that led to an ancient jellyfish’s preservation and may offer clues to understanding odd sand deposits found elsewhere.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHarmless bacterium edges out intestinal germ
Researchers treated C. difficile infections in mice with a closely related bacteria that blocks C. difficile growth.
-
 Life
LifeCells make their move with their ‘skeletons’
A close look at exactly what makes cells move could lead to better defenses against the spread of cancer and improved wound healing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInvasion drives quick evolution of lizard feet
After Florida islands were invaded by the Cuban anole, indigenous Carolina anoles quickly evolved feet better suited for climbing high.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCocoa antioxidants boost the aging brain
High doses of cocoa flavanols can improve some types of brain function in older individuals, a new study shows.
-
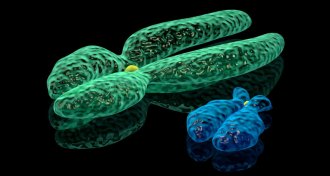 Genetics
GeneticsMen who lose Y chromosome have high risk of cancer
Losing the Y chromosome in blood cells may bring on cancer and shorten men’s lives.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow female ferns make younger neighbors male
Precocious female ferns release a partly formed sexual-identity hormone, and nearby laggards finish it and go masculine.
By Susan Milius