Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeStudy finds lack of evidence for infanticide link to monogamy
A new study contradicts idea that the rise of infanticide among mammals drove the evolution of monogamy.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsGiant otters hum, scream, say ‘hah’ and more
Often overlooked as vocalists, giant otters make 22 different calls as adults and 11 kinds of baby babble.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStopped brain clock saves memory in hamsters
Broken timekeeper in brain may explain some memory problems, hamster study suggests.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsFew humans were needed to wipe out New Zealand’s moa
A new study finds that the Maori population was still small when it managed to drive several species of large, flightless birds extinct.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRare mutations may protect against heart disease
Rare mutations in a key gene seem to lower bad cholesterol and provide protection against heart disease.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFoul smells during sleep may help smokers quit
A night of smelling rotten eggs and fish while inhaling cigarette odors makes smokers reach for fewer cigarettes upon waking.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSnake moms-to-be crave toxic toads
The snake Rhabdophis tigrinus seeks out toxic toads to eat when breeding. The snakes can then pass the poisons on to her offspring as chemical defenses.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSerotonin lies at the intersection of pain and itch
Serotonin may help relieve pain, but it also causes itch. A study shows why scratching just makes it worse.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHuman thoughts control mouse genes
Human brain waves trigger light that activates protein production in rodents.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChronic marijuana use may alter the brain
Long-term marijuana use may lead to reduced gray matter and increased white matter connectivity in the brain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes tell tale of cat domestication
A peek into cats’ genetic makeup may help reveal how hissing wild felines became purring tabbies.
-
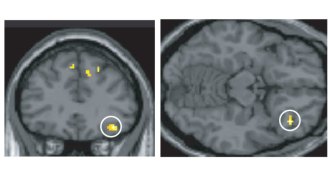 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain regions linking odors to words pinpointed
Scientists have pinpointed two brain regions involved in linking odors to their names, with implications for why smells are hard to identify.