Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
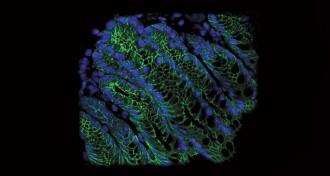 Microbes
MicrobesThe year in microbiomes
This year, scientists pegged microbes as important players in several aspects of human health, including obesity and cancer.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsStarving mantis females lie to make a meal of a male
When in desperate straits, a female false garden mantid turns into a femme fatale, emitting false chemical cues that lures in a male to eat.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIt’s bat vs. bat in aerial jamming wars
In nighttime flying duels, Mexican free-tailed bats make short, wavering sirenlike sounds that jam each other’s sonar.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsLucky break documents warbler tornado warning
Warblers fitted with data collecting devices for other reasons reveal early and extreme measures when dodging April’s tornado outbreak.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsCrows may be able to make analogies
Crows with little training pass a lab test for analogical reasoning that requires matching similar or different icons.
By Susan Milius -
 Agriculture
AgricultureRestoring crop genes to wild form may make plants more resilient
Restoring wild genes could make plants more resilient in tough environments.
-
 Life
LifeFast test reveals drug-resistant bacteria
A new test uses time-lapse photography to see within a few hours whether individual bacterial cells are vulnerable to antibiotics.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsEvolve and Linkage turn science into games
In the two new games Evolve and Linkage, biological principles are made entertaining and strategic.
-
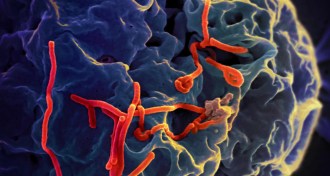 Microbes
MicrobesYear in review: Science faces Ebola epidemic
West Africa’s 2014 Ebola epidemic showed what can happen when a contagious virus emerges where cultural practices, public fears and porous borders fuel the spread of disease.
By Nathan Seppa -
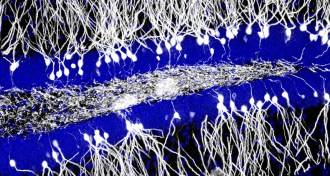 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Memories vulnerable to manipulation
New experimental results in 2014 helped bring scientists closer to understanding how the brain manipulates memories to make sense of the world.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCocoa antioxidant sweetens cognition in elderly
Very high doses of antioxidants found in cocoa may prevent some types of cognitive decline in older adults. But that’s not an excuse to eat more chocolate.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Young blood aids old brains
Ingredients in young blood can rejuvenate old mice’s bodies and brains, scientists reported in 2014.