Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCockroach personalities can speed or slow group decisions
The mix of temperaments in an alarmed cluster of cockroaches changes how quickly they make group decisions.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansBaby brains undergo dramatic changes in utero
Developing human brains experience more than 28,000 changes in a molecular process that governs gene activity.
-
 Plants
PlantsIsaac Newton’s theory of how water defies gravity in plants
A passage in one of Isaac Newton’s journals reveals that he may have theorized basic plant hydrodynamics long before botanists.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMigrating ibises take turns leading the flying V
During migration, ibises flying in a V formation cooperate and take turns flying in wake to save energy, a new study suggests.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming Arctic will let Atlantic and Pacific fish mix
The ultra-cold, ice-covered Arctic Ocean has kept fish species from the Atlantic and Pacific separate for more than a million years — but global warming is changing that.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a spider spins electrified nanosilk
The cribellate orb spider (Uloborus plumipes) hacks and combs its silk to weave electrically charged nanofibers, a new study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChicks show left-to-right number bias
Recently hatched chicks may have their own version of the left-to-right mental number line.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsPregnancy in mammals evolved with help from roving DNA
DNA that “jumped” around the genome helped early mammals shift from laying eggs to giving birth to live young.
-
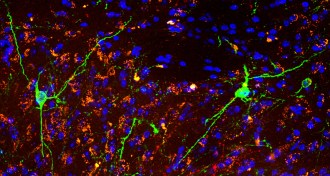 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNewly identified brain circuit could be target for treating obesity
In mice, specific nerve cells control compulsive sugar consumption, but not normal feeding, hinting at a new therapeutic target for treating obesity.
-
 Plants
PlantsPlant chemical weaponry may offer ammunition for pesticides
Chemicals produced by two plant species disrupt insect hormone pathways and could be developed in to efficient, safe pesticides.
-
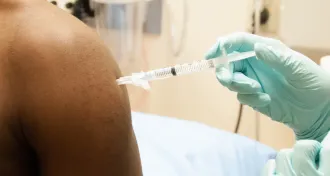 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola vaccine performs well in U.K. human trial
A vaccine that protects against the Zaire strain of Ebola turns in promising preliminary results from a human trial.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySmell circuitry, stalled stem cells and more reader feedback
Readers discuss a journal's publishing practices, ask about the human sense of smell and weigh in on their favorite picks from our Top 25 stories of the year.