Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
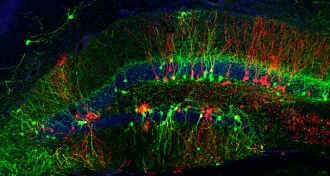 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWith good timing, experiences can rewire old brains
New experiences can rewire old brains — but the timing has to be just right.
-
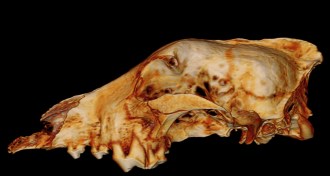 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient wolf skulls challenge dog domestication timeline
A 3-D analysis of two ancient canine skulls from Russia and Belgium suggests the fossils were of wolves, not dogs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTropical wasps memorize friendly faces
A social wasp species uses sight and smell to keep intruders from hijacking their nests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow the brain sees follow-through
The follow-through on your golf swing is more than just a way to use up extra energy. It’s part of how your brain “sees” a movement.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMonkeys reached Americas about 36 million years ago
Peruvian fossils suggest ancient African primates somehow crossed the Atlantic Ocean and gave rise to South American monkeys.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsHuge, hollow baobab trees are actually multiple fused stems
The trunk of an African baobab tree can grow to be many meters in diameter but hollow inside. The shape, researchers say, occurs when several stems fuse together.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCockroach personalities can speed or slow group decisions
The mix of temperaments in an alarmed cluster of cockroaches changes how quickly they make group decisions.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansBaby brains undergo dramatic changes in utero
Developing human brains experience more than 28,000 changes in a molecular process that governs gene activity.
-
 Plants
PlantsIsaac Newton’s theory of how water defies gravity in plants
A passage in one of Isaac Newton’s journals reveals that he may have theorized basic plant hydrodynamics long before botanists.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMigrating ibises take turns leading the flying V
During migration, ibises flying in a V formation cooperate and take turns flying in wake to save energy, a new study suggests.
-
 Climate
ClimateWarming Arctic will let Atlantic and Pacific fish mix
The ultra-cold, ice-covered Arctic Ocean has kept fish species from the Atlantic and Pacific separate for more than a million years — but global warming is changing that.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a spider spins electrified nanosilk
The cribellate orb spider (Uloborus plumipes) hacks and combs its silk to weave electrically charged nanofibers, a new study suggests.