Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFlamboyant old bustards keep showing off
Among outrageously flirtatious birds called houbara bustards, old males may pay a penalty for years of extreme display.
By Susan Milius -
 Psychology
PsychologyGene variant may foretell success in program for at-risk kids
Disruptive children with DNA twist show biggest turnaround with 10-year intervention.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsOcean animals have bulked up since ancient eras
Marine animals today are much larger on average than they were in the Cambrian Period.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsBluebird moms inadvertently fuel wars between species
Extra hormones delivered to eggs holding sons in tough times end up driving one bluebird species to chase off another
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsCliff swallow breeding thwarted by bird version of bedbugs
A 30-year study of cliff swallows in Nebraska finds that the birds will abandon nests, rather than have a second brood, when their homes are infested with swallow bugs.
-
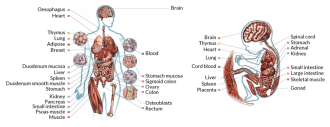 Genetics
GeneticsCatalog of DNA modifications produces surprises
A map of chemical modifications of DNA and its associated proteins shows how the genome changes during development and disease.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBlame pot munchies on nerve cells that normally nix appetite
Pot munchies demystified: Marijuana hijacks fullness nerve cells, making them send hunger signals instead.
-
 Life
LifeInsulin-suppressing hormone discovered
A newly discovered hormone suppresses insulin production and secretion in fruit flies and maybe in humans.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFooled you! Whirling tails of luna moths deflect bat attacks
Luna moths can use their tails to reflect the echolocation pings of bats, tricking the predators into striking the tails instead of less expendable body parts.
By Susan Milius -
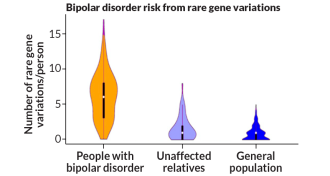 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBipolar risk boosted by accumulation of rare versions of genes
A buildup of rare versions of genes that control nerve cell activity contributes to the genetic risk of bipolar disorder.
-
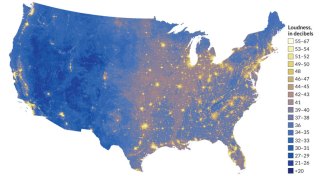 Environment
EnvironmentA coast-to-coast picture of America’s cacophony of sounds
The National Park Service mapped noise across the United States.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsFor penguins, it’s a matter of no taste
Penguins lack taste genes for bitter, sweet and umami.