Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
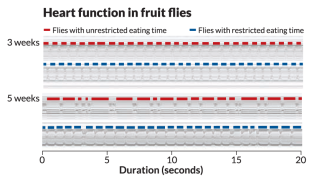
LifeFor healthy eating, timing matters
Limiting eating times improves heart function in fruit flies.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSniffing out human pheromones
A new review argues that most of the chemicals labeled human pheromones, and the experiments behind them, don’t pass the smell test.
-
 Neuroscience
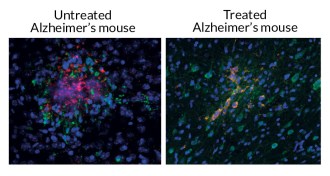
NeuroscienceUltrasound attacks Alzheimer’s plaques
A new study offers clues to how ultrasound may work as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
-
 Paleontology
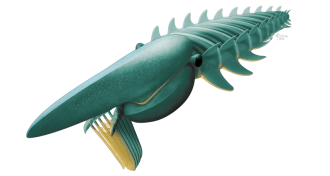
PaleontologyHow arthropods got their legs
New fossils reveal how arthropods evolved branching limbs.
-
 Life
LifeChickens to blame for spread of latest deadly bird flu
Chickens are responsible for the second wave of H7N9 bird flu in China.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFlowers make the menu for nearly all Galapagos birds
Almost every species of Galapagos land bird has been found feeding on the nectar and pollen of flowers. Such an expansion of diet has never before been observed.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElectrical zap of cells shapes growing brains
The electric charge across cell membranes directs many aspects of brain development, and changing it can fix certain brain birth defects.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMapping aggression circuits in the brain
Using optogenetics and other techniques, scientists are tracing connections to and from the brain’s aggression command center.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Life
LifeExperimental herpes vaccine works in mice
An experimental herpes vaccine works in animal tests by using an approach starkly different from that used in previous vaccine development.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsHummingbird may get promoted
Not just a subspecies: A flashy, squeaky hummingbird should become its own species, ornithologists argue.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeLife’s origin might illustrate the power of game theory
Game theory math can describe molecular competition and cooperation, perhaps providing clues to the origin of life.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPossible ancestor of sponges found
An exquisitely preserved 600-million-year-old fossil from China has cell types and a shape resembling sponges, thought to be among the first multicellular animals to evolve.
By Susan Milius