Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil of monstrous fish-eating amphibian unearthed
A new Triassic species of giant amphibian lived like a crocodile instead of like its cute little salamander and frog relatives of today.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsPiggyback rides and other crocodile fun
We don’t know the playful side of crocodiles perhaps only because we haven’t looked.
By Susan Milius -
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘The Invaders’ sees dogs as key to modern humans’ success
Neandertals went extinct when Homo sapiens transformed wolves into hunting aids, author proposes.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsConservationists should make friends with hunters
A survey of outdoor enthusiasts in rural New York finds that both hunters and birdwatchers are likely to engage in conservation behaviors, such as donating money.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy orangutans cup their mouths to sound an alarm
Orangutans might use their hands to lower the pitch of alarm calls, a study suggests.
-
 Life
LifeTurning the gut microbiome into a chat room
Bacterial communication molecules can help shape microbial communities after antibiotics.
-
 Animals
AnimalsParasites make cannibal shrimp hungry
Parasites make sometimes-cannibalistic shrimp more cannibalistic, a new study suggests.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFearsome croc called the Carolina Butcher once ruled the north
Early ancestors of crocodiles, not dinosaurs, may have been northern Pangaea’s top predator 230 million years ago, according to a new fossil find.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineProspective Crohn’s drug yields high rate of remission
An experimental Crohn’s disease drug triggers a high remission rate in patients.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
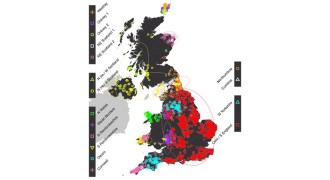
GeneticsHistory of the United Kingdom revealed in its genes
A genetics study finds subtle differences that reveal secrets about the history and ancestry of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
-
 Humans
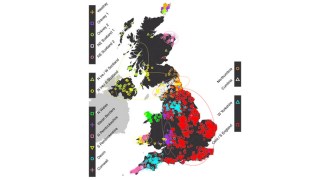
HumansHistory of the United Kingdom revealed in its genes
A genetics study finds subtle differences that reveal secrets about the history and ancestry of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow velvet worms slime their prey
Researchers have figured out the mechanics behind velvet worms’ wobbly slime jets.