Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Plants
PlantsBits of bacterial DNA naturally lurk inside sweet potatoes
Samples of cultivated sweet potatoes worldwide carry DNA from Agrobacterium cousin of bacterium used for GMOs.
By Susan Milius -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsBefore you plant this spring, consider the birds
A study of Chicago neighborhoods finds that the plants in private yards influence the variety of birds that live in the area.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTales of the bedbug, one of the world’s most reviled insects
‘Infested’ captivates with stories about the bloodsucking insects. Resurgent in many areas in the United States, bedbugs are the fastest-growing moneymaker in pest control.
By Sid Perkins -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSky’s brilliant hues may help bodies keep time
The internal clocks of mice are sensitive to changes in the sky’s colors. Humans’ clocks may work similarly, offering a tool to trump jet lag.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBeing watched can boost productivity
In the company of another, a monkey steps up production on a simple job.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGazing deeply into your dog’s eyes unleashes chemical attraction
Dogs and people gazing into each other’s eyes give each other a bond-strengthening rush of oxytocin.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeOctopuses move with uncoordinated arms
An octopus crawls unlike any other animal. Mimicking the cephalopod’s control over its movements may lead to more agile robots.
-
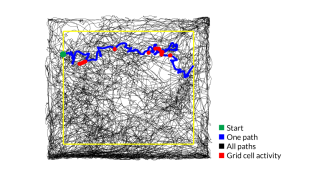 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhen brain’s GPS goes awry, barriers can reboot it
Brain’s internal map self-corrects when it hits a (literal) wall.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow many manatees live in Florida?
The most recent official count reports more than 6,000 manatees in Florida waters, but a new estimate may give a better picture of the population.
-
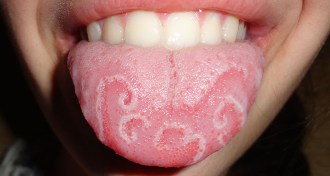 Life
Life‘Geographic tongue’ creates unique topography
A condition called ‘geographic tongue’ makes mouth organ appear maplike.
-
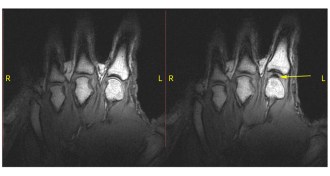 Life
LifeResearchers pull fingers to solve why knuckles crack
Knuckle cracking is the sound of a bubble forming in a joint, MRI images reveal.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSame mutations can show up in tumors, healthy tissues
Analyzing samples of healthy and tumor tissues could pinpoint which mutations are driving cancer and help develop better-targeted treatments.
By Nathan Seppa