Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
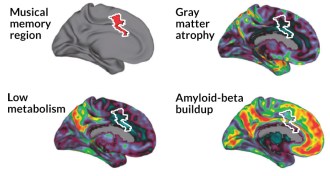
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s spares brain’s music regions
Brain regions involved in recognizing familiar songs are relatively unscathed in Alzheimer’s disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPigs don’t deserve the name ‘Lesser Beasts’
From ancient forests to modern farms, pigs’ relationship with humans has been symbiotic.
-
 Life
LifeAging: Nature’s way of reducing competition for resources
Aging may have developed in many species as a genetic mechanism to conserve future resources. If the controversial proposal is true, then scientists may be able to greatly extend life span by deactivating the machinery for aging embedded in our DNA.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsCould the dinos of ‘Jurassic World’ become invasive?
Even if they escaped their island home, the giant reptiles of ‘Jurassic World’ probably wouldn’t survive on the mainland. But the movie’s plants are another story.
-
 Genetics
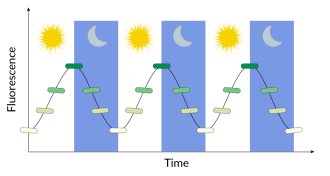
GeneticsA circadian clock transplant gives E. coli rhythm
Clockworks from algae built into E. coli may hold future jet lag treatment.
-
 Life
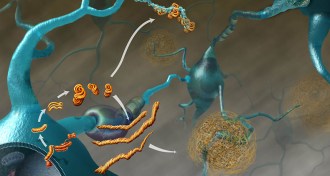
LifeA protein variant can provide protection from deadly brain-wasting
If cannibalism hadn’t stopped, a protective protein may have ended kuru anyway.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNewly discovered tiny frogs live on islands in the sky
Scientists find seven new species of frogs in southern Brazil, and more could be waiting, they say.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyBronze Age humans racked up travel miles
A new study indicates long journeys and unexpected genetic links in Bronze Age Eurasian cultures.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChimps get buzzed on fermented tree sap
Scientists have documented the first case of chimpanzees drinking ethanol in the wild.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew analysis cuts massive dino’s weight in half
Gigantic dinosaur Dreadnoughtus may have weighed only about half of what scientists estimated last year.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyTraces of dino blood, soft tissue found even in junk bones
Hints of blood and collagen found in poorly preserved dinosaur bones suggest that soft tissue from the creatures may be easier to come by.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCamera traps provide treasure trove of African animal pics
Scientists set up hundreds of cameras across Serengeti National Park to capture images of predators and their prey.