Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyTraces of dino blood, soft tissue found even in junk bones
Hints of blood and collagen found in poorly preserved dinosaur bones suggest that soft tissue from the creatures may be easier to come by.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCamera traps provide treasure trove of African animal pics
Scientists set up hundreds of cameras across Serengeti National Park to capture images of predators and their prey.
-
 Life
LifeMERS virus didn’t morph in its move to South Korea
No obvious changes in the MERS virus account for its rapid spread in South Korea.
-
 Life
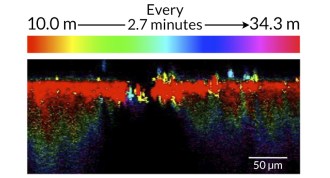
LifeTracing molecules’ movement in nails may help fight fungus
Tracking chemicals through the human nail may provide valuable insight for drug development.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHorned dino aside, here are some other fun fossil finds
Here's a roundup of some fossil finds reported this week.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Virgin births’ won’t save endangered sawfish
Sawfish are the first wild vertebrates found to reproduce via parthenogenesis.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFemale’s nose blocks scent of a male
When a female mouse is in an infertile stage of her reproductive cycle, her nose cells don’t alert her brain to the presence of a potential mate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFly spit protein holds back parasite infection in monkeys
A protein called PdS15 found in the saliva of the sand fly that spreads leishmaniasis may be used in a vaccine to combat the parasitic scourge causing the illness.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyTriceratops relative reveals dino diversity
A newly discovered relative of Triceratops provides new insight into the evolution of horned dinosaurs.
-
 Genetics
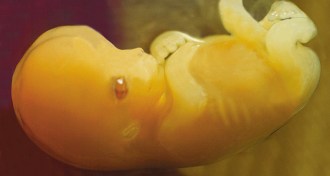
GeneticsDNA tags mostly deleted in human germ cells
Human embryos come with some heavy-duty erasers. Chemical tags on DNA get mostly wiped out in the womb.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnant male pipefish not so great at giving embryos oxygen
During male pregnancy, pipefish embryos can get stunted by low oxygen in dad’s brood pouch.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsAfrican herbivores share space but not diet
Large herbivorous mammals on the plains of Kenya have distinctive diets, a new study finds.