Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
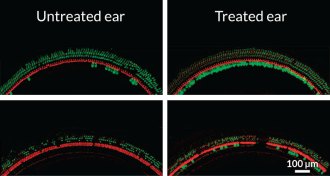
GeneticsGene therapy restores hearing in mice
Scientists have used gene therapy to restore hearing in deaf mice.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCuckoos may have a long-lasting impact on other birds
Some birds that don’t have to worry about parasites like cuckoos reject eggs that aren’t their own. It might be a legacy of long-ago parasitism.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew cases of Ebola emerge in Liberia
Liberia has recorded three new Ebola cases after being declared free of the disease in May.
-
 Life
LifeAge isn’t just a number
Getting old happens faster for some, and the reason may be in the blood.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSeabirds may navigate by scent
Shearwaters may use olfactory cues to find islands far across the open ocean, a new study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhy mammoths loved the cold
An altered temperature sensor helped mammoths adapt to the cold.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy seahorses have square tails
3-D printed seahorse tails reveal possible benefits of square cross-sections for armor and gripping.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWrinkled brain mimics crumpled paper
Brains crumple up just like wads of paper, a new study suggests.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryMissing enzyme to blame for scentless roses
The unusual enzyme behind roses’ sweet smell may help researchers revive the flower’s potent aroma.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeGenetic tweak hints at why mammoths loved the cold
An altered temperature sensor helped mammoths adapt to the cold.
-
 Health & Medicine
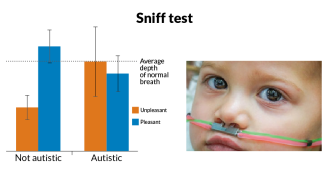
Health & MedicineSmell test may detect autism
A quick sniff test could reveal whether or not a child has autism, but some scientists have doubts.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsCentipede discovered in caves 1,000 meters belowground
A newly discovered centipede species lives deep underground.