Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeTrees are failing to adapt to climate change. Losing fungi partners may be why
Certain fungi give trees nutrients and water, but heat and drought are putting both at risk.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsNew videos reveal the hidden lives of Andean bears
The footage give clues to the range of plants the bears eat and how they mate, information important for conservation.
-
 Life
LifeHere’s how long it would take 100 worms to eat the plastic in one face mask
An experiment reveals that a bio-solution to humans’ microplastics mess is likely to fall short, but could inspire other ways to attack the problem.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsEthiopian wolves are the first large carnivores found to slurp nectar
Wolves from three different packs were seen licking red hot poker flowers. That sweet tooth could make them the first known large predator pollinators.
-
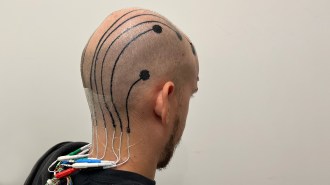 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElectronic ‘tattoos’ offer an alternative to electrodes for brain monitoring
A standard EEG test requires electrodes that come with pitfalls. A spray-on ink, capable of carrying electrical signals, avoids some of those.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant hornets have been sighted in Europe for the first time
Four southern giant hornets have turned up in Spain. Similar stingers, known for honeybee attacks, had the Pacific Northwest on edge a few years ago.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsVideos capture orcas’ tricks for taking down the largest fish on Earth
Citizen science videos document for the first time how orcas coordinate an attack against whale sharks.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThis ‘hidden figure’ of entomology fought for civil rights
Margaret S. Collins, the first Black American female entomologist to earn a Ph.D., overcame sexism and racism to become a termite expert.
By Susan Milius -
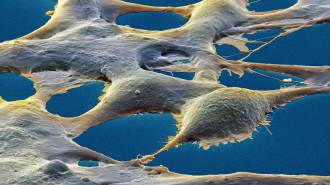 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLike brain cells, kidney cells can form memories
Scientists found memory’s molecular machinery at work in cells outside the nervous system.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyChina’s famously rich dinosaur fossil beds get a new origins story
Cave-ins and floods may have buried the Cretaceous creatures of the fossil Jehol Biota rather than volcanic eruptions, a new study claims.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDengue is classified as an urban disease. Mosquitoes don’t care
Infectious diseases are often labeled “urban” or “rural.” Applying political labels to public health misses who is at risk, experts argue.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsFor adult chimps, playing may be more important than previously thought
A multiyear study of dozens of wild, adult chimps suggests that play helps reduce tension and boost cooperation among individuals.