Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeFor people, mealtime is all the time
People eat for most of their waking hours, which may affect sleep and weight.
-
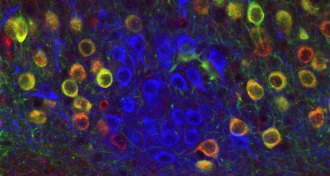 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSeparate cell types encode memory’s time, place
Cells called ocean cells help store a memory’s “where,” while other cells called island cells help store a memory’s “when.”
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow to see sea turtles — without bothering them
Sea turtles come out of the water to lay eggs on beaches. It’s a great time to see the reptiles — if you know what you are doing.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese fish would rather walk
Slowpokes of the sea, frogfish and handfish creep along the ocean bottom.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsBenyam Kinde: Gene expression and Rett syndrome
M.D.-Ph.D. student Benyam Kinde studies how genetic changes affect brain cells’ activity in Rett syndrome.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIsaac Kinde: Finding cancer via altered genes
Isaac Kinde helped create a technology that can spot cancers early to give patients a better chance at survival.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePriya Rajasethupathy: Memories mark DNA
Neuroscientist Priya Rajasethupathy has discovered a tiny molecule that may turn off part of the genome to help the brain store long-term memories.
By Erin Wayman -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSteve Ramirez: Erasing fear memories
Neuroscientist Steve Ramirez is manipulating memories in mice to one day erase fearful memories of PTSD.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYasser Roudi: Creating maps in the brain
Physicist Yasser Roudi does the math on how the brain and other complex systems process information.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Life
LifeGia Voeltz: Redrawing the cell’s floor plan
Cell biologist Gia Voeltz has changed our view of the endoplasmic reticulum.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsFeng Zhang: Editing DNA
Scientist Feng Zhang has developed a system to easily and precisely edit genomes.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Animals
AnimalsBlue-footed boobies dirty their eggs to hide them from predators
Blue-footed boobies lay bright white eggs on the ground. Dirtying the eggs camouflages them against gulls, a new study finds.