Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: Fluke extinction surprises lab
A die-off of bacteria in a carefully controlled lab experiment offered an evolutionary lesson this year: Survival depends not only on fitness but also on luck.
-
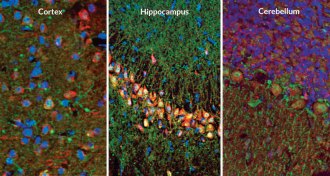 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Gaps in brain nets might store memories
Holes in nets that surround nerve cells may store long-term memories, scientists proposed this year.
-
 Life
LifeScience explains what makes dogs such sloppy drinkers
There’s hidden precision in the splashy mess of a dog drinking.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsForgetful male voles more likely to wander from mate
Poor memory linked to a hormone receptor in the brain could make male prairie voles more promiscuous.
-
 Plants
PlantsSingle gene influences a petunia’s primary pollinator
Mutations on a single gene determine how much ultraviolet light a petunia flower absorbs, and in turn, which animal pollinates the flower.
-
 Life
LifeTo push through goo, use itty, bitty propellers
Newly designed micropropellers mimic bacteria to move through viscous surroundings.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNew movie asks viewers to care about whale hunters. Will they?
A new movie tells the tale of sailors shipwrecked by a whale. But it’s hard to feel sorry for the people trying to kill the animal.
-
 Life
LifeMicrobes show up on schedule after death
Microbes in the soil beneath dead bodies offer forensic clues for time and place of death.
By Meghan Rosen -
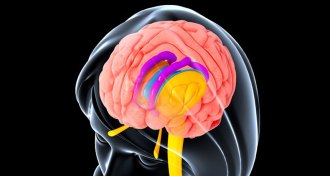 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain shapes come from mom and dad
By linking genes to brain shapes, scientists have a new way to study how the brain works.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome warblers make their long winter migration even longer
Blackpoll warblers in western North America head east to fatten up before their transoceanic migration.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPlayful pups conceived via in vitro fertilization for the first time
Scientists have solved the mystery of how to perform in vitro fertilization in dogs, which could help rid canines of heritable diseases.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsLiberia’s Ebola outbreak largely traced to one source
Ebola’s spread and evolution in Liberia echoes patterns seen in Sierra Leone.