Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFDA predicts no significant environmental impact from GM mosquitoes
The FDA has taken a step in the process of deciding whether to allow the first test release in the United States of genetically modified mosquitoes to fight diseases such as Zika.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s how dust mites give dermatitis sufferers the itch
Dust mites can make people with eczema truly miserable. Now, scientists have figured out why they make some people scratch, and resolved a dermatological debate.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny hummingbirds can fly a long, long way
Some ruby-throated hummingbirds may be capable of flying more than 2,000 kilometers without stopping, scientists calculate.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow to keep seagrasses as happy as a clam
Drought can do more damage to seagrass meadows if their partnership with clams break down.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsGreat tits sing with syntax
Humans are no longer the only species to use compositional syntax. Great tits do, too.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceReaders respond to stress, tattoos, and the universe
Stress, tattoos, cosmic origins and more reader feedback.
-
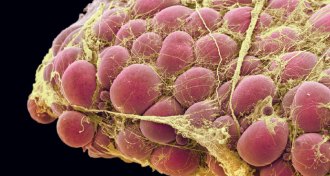 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCells from fat mend bone, cartilage, muscle and even the heart
Stem cells and other components of fat can be coerced to grow into bone, cartilage, muscle or to repair the heart.
By Susan Gaidos -
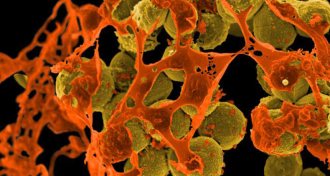 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMolecules found to counter antibiotic resistance
Molecules made in a lab can foil antibiotic resistance in bacteria.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew techniques regrow lens, cornea tissue
Preliminary stem cell discoveries may restore lenses and corneas.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyH. erectus cut, chewed way through evolution
A diet that included raw, sliced meat changed the face of early Homo evolution, scientists say.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
OceansSwirls of plankton decorate the Arabian Sea
The dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans is taking over in the Arabian Sea, posing a potential threat to its ecosystem.
-
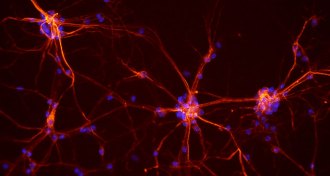 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceScientists still haven’t solved mystery of memory
50 years have refined a basic understanding of the brain, but scientists are still exploring how memories form, change and persist.