Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Plants
PlantsNightshade plants bleed sugar as a call to ants for backup
Bittersweet nightshade produces sugary wound goo to lure in ant protectors that eat herbivores, researchers have found.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDragons sleep like mammals and birds
Some lizards may sleep in the same way as mammals and birds, a new brain wave study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIons may be in charge of when you sleep and wake
The recipe for sleep and wake may depend on ions.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChemical behind popcorn’s aroma gives a bearcat its signature scent
Bearcats smell like popcorn. Now scientists now why: The chemical responsible for popcorn’s alluring scent has been found in bearcat pee.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPeacocks twerk to shake their tail feathers
Researchers reveal the biomechanics of the peacock mating dance.
-
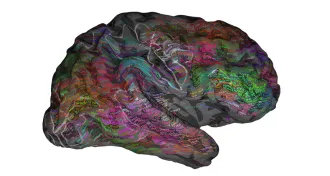 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWords’ meanings mapped in the brain
Language isn’t just confined to one region of the brain: The meaning of words spark activity all over the cerebral cortex.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsHow animal poop could be key in solving echidna mystery
The western long-beaked echidna hasn’t been seen in Australia in 10,000 years. But DNA in scat could reveal its presence.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBeetle saved in amber had helicopter wings
For the first time, scientists report the fossilized remains of two tiny Jacobson’s Beetles, preserved in amber for at least 37 million years.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFindings on wobbly memories questioned
In contrast to older studies, new results suggest that new memories don’t interfere with older, similar ones.
-
 Plants
PlantsPrions may help plants remember
A plant protein has passed lab tests for prionlike powers as molecular memory.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsPlants might remember with prions
A plant protein has passed lab tests for prionlike powers as molecular memory.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeUncertainty is stressful, but that’s not always a bad thing
Life is full of stressful, ambiguous situations. But a new study shows that the ones we can predict stress us out less, and may even help us learn.