Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNew analysis: Genetically engineered foods not a health risk
No real evidence for health or environmental dangers of GE crops.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeHow the Galápagos cormorant got its tiny wings
Galápagos cormorants’ tiny wings may be due to altered reception in cellular antennas.
-
 Life
LifeGiraffe’s long neck linked to its genetic profile
Giraffes’ genes may reveal how their necks grew long and hearts got strong.
-
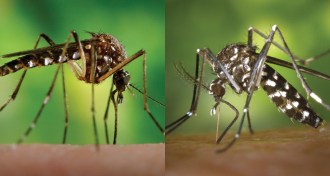 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists wrestle with possibility of second Zika-spreading mosquito
It’s hard to say yet whether Asian tiger mosquitoes will worsen the ongoing Zika outbreak in the Americas.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
Animals‘America’s Snake’ chronicles life and times of iconic timber rattlesnake
America’s Snake looks past timber rattlesnake’s fearsome reputation and delves into the fascinating biology of this iconic serpent.
By Sid Perkins -
 Genetics
GeneticsFaulty gene can turn colds deadly for babies, toddlers
Children with a faulty virus-sensing gene may land in intensive care after a cold.
-
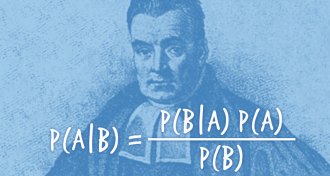 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBayesian reasoning implicated in some mental disorders
An 18th century math theory may offer new ways to understand schizophrenia, autism, anxiety and depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves in REM sleep help store memories
Mice with disturbed REM sleep show memory trouble.
-
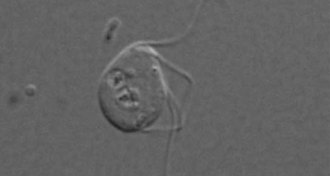 Life
LifeGut microbe may challenge textbook on complex cells
Science may finally have found a complex eukaryote cell that has lost all of its mitochondria.
By Susan Milius -
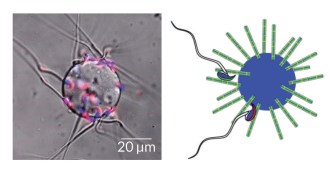 Life
LifeHow to trap sperm
Lab-made beads can trick and trap sperm, potentially preventing pregnancy or selecting sperm for fertility treatments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouse studies link Zika virus infection to microcephaly
Three new studies in mice shore up the link between microcephaly and Zika virus infection.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: First mouse study proof that Zika causes microcephaly
Three new studies in mice shore up the link between microcephaly and Zika virus infection.
By Meghan Rosen