Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese lizards bleed green
Blood and bones turn naturally green in island lizards. Their evolutionary history still needs explaining.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient reptiles saw red before turning red
The discovery that birds and turtles share a gene tied to both color vision and red coloration is more evidence that dinosaurs probably saw the color red — and perhaps were even red, too.
-
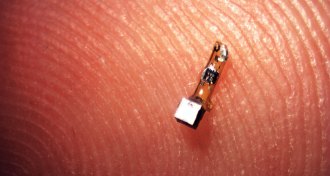 Neuroscience
Neuroscience‘Neural dust’ can listen to body’s electrical signals
Tiny crystals can detect electrical signals in nerves and muscles of rats.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySea life stars in museum’s glass menagerie
See Leopold and Rudolf Blaschkas’ delicate glass jellyfish, anemones, sea worms and other marine invertebrates at the Corning Museum of Glass.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFDA OKs first GM mosquito trial in U.S. but hurdles remain
The FDA has concluded that test releases of Oxitec GM mosquitoes on a Florida key poses no significant problem for the environment, but local officials still have to agree
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew fossil suggests echolocation evolved early in whales
A 27-million-year-old whale fossil sheds light on echolocation’s beginnings.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRats offer clues to biology of alcoholism
Heavy-drinking rats are giving scientists new genetic clues to alcoholism.
-
 Plants
PlantsInternal clock helps young sunflowers follow the sun
A circadian clock helps sunflowers follow the sun’s daily path across the sky
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceRed blood cells sense low oxygen in the brain
Red blood cells sense low oxygen and speed to the scene, a new study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSmart mice have better odds of survival
African striped mice (Rhabdomys pumilio) may survive summer droughts by their wits, a study suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBird-friendly yards have a major downside — for birds
Vegetation and feeders bring birds into our yards. But those lures also bring more birds to collide with the windows in our homes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDiversity of indoor insects, spiders adds to life’s luxuries in high-income neighborhoods
A massive survey of indoor spiders and insects in town finds dozens of different scientific families in homes, more in high-income neighborhoods.
By Susan Milius