Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLizard mom’s microbiome may protect her eggs
Striped plateau lizard moms don’t do any parenting beyond laying eggs. But they may convey protection from pathogens with help from their microbiome.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFemale fish have a fail-safe for surprise sperm attacks
A Mediterranean fish provides evidence that, even after laying their eggs, females can still influence who fertilizes them.
-
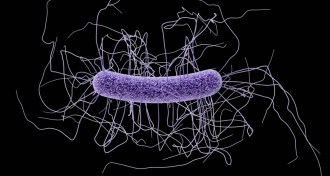 Life
LifeGenes that control toxin production in C. difficile ID’d
Pinpointing the genes behind Clostridium difficile toxin production could help researchers disarm the superbug without killing “good” bacteria.
-
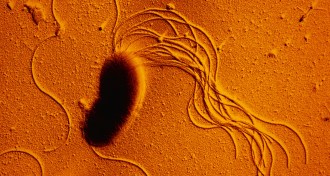 Life
LifeTwo stationary kinds of bacteria can move when mixed
Bacteria stuck when alone on a dry surface get moving — and get faster — when they evolve together.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeFor bacteria, assassination can breed cooperation
Cholera bacteria stabbing each other can encourage the evolution of cooperation.
By Susan Milius -
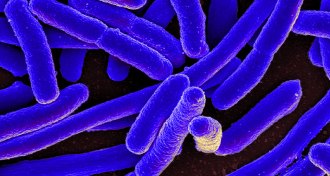 Life
Life‘Promiscuous’ enzymes can compensate for disabled genes
Promiscuous enzymes can step in when bacteria lose genes they need to function.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCapybaras may be poised to be Florida’s next invasive rodent
Some capybaras have escaped their owners in Florida. Others have been set loose. Now there are fears the giant rodents could become established in the state.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnemone proteins offer clue to restoring hearing loss
Proteins that sea anemones use to regenerate may help restore damaged hearing in mammals.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSleep deprivation hits some brain areas hard
Brain scan study reveals hodgepodge effects of sleep deprivation.
-
 Animals
AnimalsStudy ranks Greenland shark as longest-lived vertebrate
Radiocarbon in eye lenses suggests mysterious Greenland sharks might live for almost 400 years.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsSneaky virus helps plants multiply, creating more hosts
Plant virus makes hosts more attractive to pollinators, ensuring future virus-susceptible plants.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMix of brain training, physical therapy can help paralyzed patients
Long-term training with brain-machine interface helps people paralyzed by spinal cord injuries regain some feeling and function.
By Meghan Rosen