Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
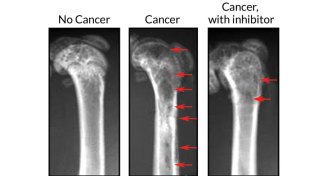
Health & MedicineWeapon of bone destruction identified
Scientists discover myeloma’s secret bone-destroying messenger.
-
 Life
LifeCRISPR inspires new tricks to edit genes
CRISPR/Cas9 has been a rockstar gene-editing tool for just four years and it’s already being tweaked to do more things better.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat Donkey Kong can tell us about how to study the brain
Neuroscience tools failed to reveal much about a simple microprocessor. What can they really tell us about the brain?
-
 Health & Medicine
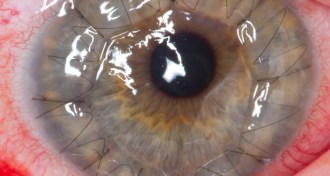
Health & MedicineCornea donation may have sex bias
Women receiving a corneal transplant do better when their donors are female, new research finds.
By Amber Dance -
 Plants
PlantsHow a tomato plant foils a dreaded vampire vine
Tomatoes can foil a dodder plant attack by getting scared and scabbing over.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsWays to beat heat have hidden costs for birds
Birds that look as if they’re coping with heat waves and climate change may actually be on a downward slide, with underappreciated disadvantages of panting and seeking shade.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsThe weird mating habits of daddy longlegs
Scientists studying the sex lives of daddy longlegs are finding there’s a lot of diversity among this group of arachnids.
-
 Oceans
OceansLack of nutrients stalled rebound of marine life post-Permian extinction
Warm sea surface temperatures slowed the nitrogen cycle in Earth’s oceans and delayed the recovery of life following the Permian extinction, researchers propose.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDarwin’s Dogs wants your dog’s DNA
The Darwin’s Dogs citizen science project is collecting canine DNA to better understand dog genetics and behavior.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBird nest riddle: Which shape came first?
Today’s simple cup-shaped songbird nests look as if they just had to have evolved before roofed nests. But that could be backward.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFentanyl’s death toll is rising
The ability of fentanyl, an opioid, to freeze chest muscles within minutes may be to blame for some overdoses, a new autopsy study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHoverflies (probably) can’t sense gravity
Acrobatic insects called hoverflies may simply use visual and airflow cues and not gravity to orient their bodies midair.