Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClean inside those bagpipes — and trumpets and clarinets
Bagpipes’ moist interiors may be the perfect breeding ground for yeasts and molds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
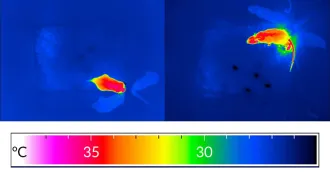
NeuroscienceCool nerve cells help mice beat heat
A new study pinpoints fever-busting cells in mice’s brains.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes help snub-nosed monkeys live the high life
Snub nosed monkeys have certain genetic variants that help them breathe easy in low oxygen.
-
 Life
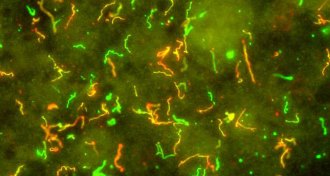
LifeLyme bacteria swap ‘catch bonds’ to navigate blood vessels
Lyme bacteria use same tricks as white blood cells to navigate blood stream.
-
 Neuroscience
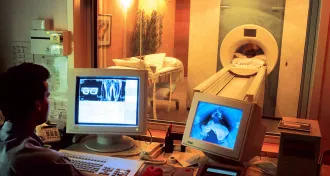
NeuroscienceComputers refine epilepsy treatment
Surgeons harnessed computers in 1966 to pinpoint source of epilepsy in the brain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThank (or blame) your genes for ability to handle java jolt
A gene involved in caffeine processing may control coffee consumption.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWarm-up benefit could explain morning birdsong
Even birds sing better after vocal warm-up, and an evolutionary arms race among rivals might have led to the intensity of the dawn chorus.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
MicrobesBacteria display qualities that a mother would love
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses big lessons we can learn from some of Earth's smallest organisms.
By Eva Emerson -
 Health & Medicine
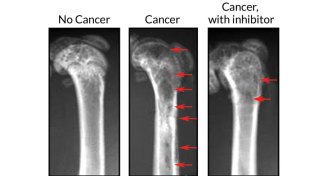
Health & MedicineWeapon of bone destruction identified
Scientists discover myeloma’s secret bone-destroying messenger.
-
 Life
LifeCRISPR inspires new tricks to edit genes
CRISPR/Cas9 has been a rockstar gene-editing tool for just four years and it’s already being tweaked to do more things better.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat Donkey Kong can tell us about how to study the brain
Neuroscience tools failed to reveal much about a simple microprocessor. What can they really tell us about the brain?
-
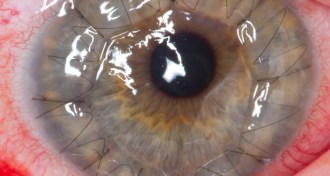 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCornea donation may have sex bias
Women receiving a corneal transplant do better when their donors are female, new research finds.
By Amber Dance