Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
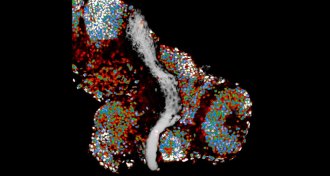
NeuroscienceBrain’s physical structure may help guide its wiring
The brain’s stiffness helps dictate how nerve cells grow, a study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsTo study Galápagos cormorants, a geneticist gets creative
To collect DNA from four cormorant species, this scientist called in bird scientists far and wide.
-
 Oceans
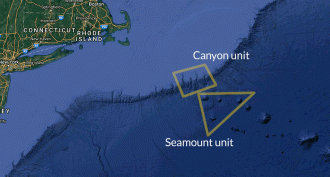
OceansFirst U.S. ocean monument named in the Atlantic
A region of ocean off the coast of Cape Cod has become the first U.S. marine national monument in the Atlantic Ocean, President Barack Obama announced.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFrog-hunting bats have ‘cocktail party effect’ workaround
Test with robotic frogs finds bats that hunt amphibians switch their attention to other clues if outside noise masks the mating chorus.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeRattlesnakes have reduced their repertoire of venoms
The most recent common ancestor of today’s rattlesnakes had a huge set of toxin-producing genes. Modern rattlesnake species have independently ditched some of these genes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHawaiian crows ace tool-user test
The almost-extinct Hawaiian crow joins the small, select flock of birds shown to use sticks tools routinely and well to wiggle bits of food out of crevices.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeColor vision strategy defies textbook picture
Cone cells in the retina see in black and white and color.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSandboxes keep chicken parasites at bay
Fluffing feathers in sand and dust prevents severe mite infections in cage-free hens.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKauai’s native forest birds are headed toward extinction
Kauai’s honeycreepers are losing their last refuges from mosquito-borne diseases that are spreading due to climate change. Some could become extinct within a decade.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPterosaurs weren’t all super-sized in the Late Cretaceous
A 77-million-year-old flying reptile may be the smallest pterosaur of the Late Cretaceous.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsAs IUCN votes on ivory trade, elephants’ future looks bleak
As the IUCN prepares to debate an end to the ivory trade, two new reports show just how poorly Africa’s elephant species are faring.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTiny structures give a peacock spider its radiant rump
Peacock spiders use pigments and complex nanostructures to achieve bright dance costumes.