Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOut-of-sync body clock causes more woes than sleepiness
The ailment, called circadian-time sickness, can be described with Bayesian math, scientists propose.
-
 Ecosystems
Ecosystems‘Citizen Scientist’ exalts ordinary heroes in conservation science
Journalist Mary Ellen Hannibal’s “Citizen Scientist” tells tales of ordinary people contributing to science.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBe careful what you say around jumping spiders
Sensitive leg hairs may let jumping spiders hear sounds through the air at much greater distances than researchers imagined.
By Susan Milius -
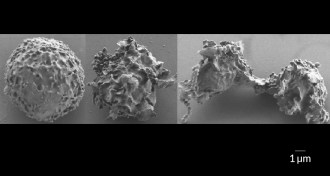 Life
LifePlacenta protectors no match for toxic Strep B pigment
Strep B uses a toxic pigment made of fat to kill immune system cells, spurring preterm labor and dangerous infections, a monkey study shows.
-
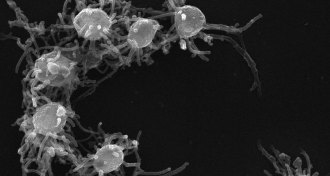 Life
LifeOne-celled life possessed tools for going multicellular
Unicellular ancestors of animals had molecular tools used by multicellular life.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow gene editing is changing what a lab animal looks like
What makes a good animal model? New techniques bring opportunities and challenges to model organisms.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHot and spicy pain signals get blocked in naked mole-rats
Naked mole-rats have a protein that interrupts pain signal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHot and spicy pain signals get blocked in naked mole-rats
Naked mole-rats have a protein that interrupts pain signal.
-
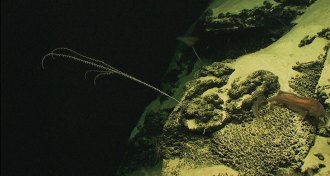 Life
LifeOcean archaea more vulnerable to deep-sea viruses than bacteria
Deep-sea viruses kill archaea disproportionately more often than bacteria, a killing spree with important impacts on the global carbon cycle.
-
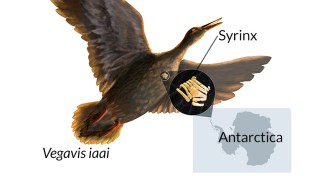 Paleontology
PaleontologyBirds’ honks filled Late Cretaceous air
Oldest avian voice box fossil yet discovered belonged to a ducklike bird that lived during the age of the dinosaurs.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsPainted lady butterflies’ migration may take them across the Sahara
The migratory patterns of painted lady butterflies are largely unknown. Now scientists have found evidence that some may migrate across the Sahara.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAfrican elephants walk on their tippy-toes
Pressure plates reveal how African elephants load their feet when they walk, providing clues to pachyderm podiatry problems.