Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHammerhead sharks’ diets may affect if they roam or stay home
Understanding hammerhead sharks’ food preferences could aid efforts to protect the critically endangered fish.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGray seals may sense their own blood oxygen levels
The seals’ ability to detect the amount of oxygen in their blood may help them make diving decisions and avoid drowning.
-
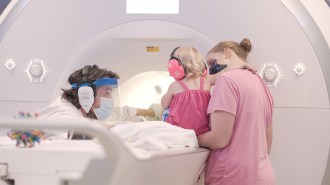 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBabies can form memories, and they do it a lot like adults
A brain scanning study of babies reveals how some of the earliest memories are made.
-
 Animals
AnimalsStinky penguin poop strikes fear into the hearts of Antarctic krill
A chemical in Adélie penguin guano may have cued krill to take evasive maneuvers in lab tests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceParrots and humans share a brain mechanism for speech
Brain activity in vocalizing budgerigar parrots showed a pattern that harkened to those found in the brains of people.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome of Sydney’s koalas are chlamydia-free, but still at risk
Southwestern Sydney's koalas have avoided the chlamydia outbreak threatening the entire species. But their isolation has left them extremely inbred.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThe mystery of how iguanas crossed the Pacific Ocean may be solved
The iguanas' 8,000-kilometer trip — one-fifth of the Earth’s circumference — is the longest made by a flightless land vertebrate.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsNarwhals may use their iconic tusks to play
Videos show narwhals using their tusks in several ways, including prodding and flipping a fish. It’s the first reported evidence of the whales playing.
-
 Life
LifeDark coats may have helped the earliest mammals hide from hungry dinosaurs
During the age of dinosaurs, early mammals probably lacked the stripes and spots of their modern relatives, having uniformly dark, drab coats.
By Jake Buehler -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceParenthood may help the brain stay young
A study of nearly 38,000 adults shows that the number of kids correlates with coordination of brain regions’ activities — regardless of parents’ sex.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine6 things to know about antidepressants
An abundance of data show that SSRIs, a class of drugs commonly used as antidepressants, are effective, though, like any drug, they have risks.
By Meghan Rosen and Laura Sanders -
 Climate
ClimateSome trees are coping with extreme heat surprisingly well
Rising temperatures could reduce trees' ability to photosynthesize. Scientists are trying to figure out just how close we are to that point.