Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
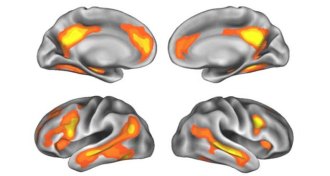
NeurosciencePregnancy linked to long-term changes in mom’s brain
Pregnancy can sculpt a mother’s brain in a way that may help her tune in to her baby.
-
 Tech
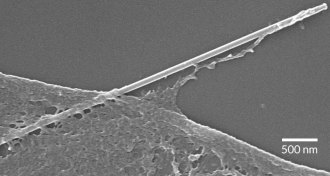
TechCells snack on nanowires
Human cells eat silicon nanowires in a process called phagocytosis. Nanowire-infused cells could be a step towards biological electronic devices.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsChimps look at behinds the way we look at faces
Humans demonstrate something called the inversion effect when gazing at faces. Chimpanzees do this too — when looking at other chimps’ butts.
-
 Genetics
Genetics50 years ago, alcohol use was linked to several gene variants
50 years later, scientists are still searching for genes that influence drinking.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsProteins that reprogram cells can turn back mice’s aging clock
Proteins that reprogram adult cells to an embryonic-like state can rejuvenate prematurely aging mice.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGenome clues help explain the strange life of seahorses
Researchers have decoded the genetic instruction manual of a seahorse (Hippocampus comes) and found clues to its nearly 104-million-year evolutionary history.
-
 Climate
ClimateArctic kelp forests may create summer refuges from ocean acidification
Long summer daylight revs up carbon capture in Arctic kelp forests, offering a little relief from acidifying ocean water.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
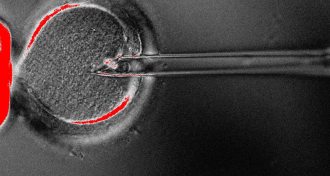
GeneticsYear in review: ‘Three-parent baby’ technique raises hope and concern
Safety and ethical concerns surround controversial mitochondrial replacement therapy.
-
 Climate
ClimateYear in review: Sea ice loss will shake up ecosystems
Researchers are studying the complex biological consequences of polar melting and opening Arctic passageways.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: How humans populated the globe
DNA studies put new twists on timing of ancient human migrations – but genetics alone are not enough to tell the full story.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
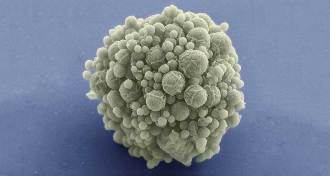
LifeYear in review: ‘Minimal genome’ makes its debut
A synthetic cell reported this year jettisons unnecessary genes and embraces human design principles.
-
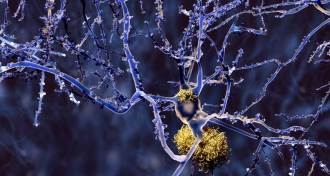 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Alzheimer’s drug may clarify disease’s origins
Researchers will now test whether a treatment that swept away amyloid brain plaques also improves cognitive performance.