Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobes survived inside giant cave crystals for up to 50,000 years
Microbes trapped in crystals in Mexico's Naica mine may represent some of the most distinct life-forms found in Earth so far.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCommon fungus may raise asthma risk
The presence of a fungus in the infant gut can signal development of asthma by age 5.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsSeagrasses boost ecosystem health by fighting bad bacteria
Seagrasses might reduce bacteria levels in ocean water.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHuman gene editing therapies are OK in certain cases, panel advises
A panel of experts says clinical gene editing to correct and prevent human disease should move forward, but enhancements should not be allowed.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil shows that ancient reptile gave live birth
A new fossil shows that a prehistoric reptile may have given birth to live young, unlike its egg-laying descendants, birds and crocodiles.
-
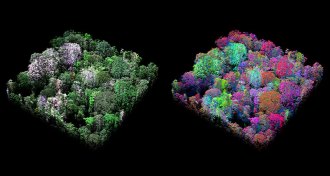 Ecosystems
EcosystemsMapping rainforest chemistry from the air reveals 36 types of forest
Aircraft analysis of tree chemicals reveals new biodiversity in the Peruvian rainforest.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe animal guide to finding love
Learn to dance, keep an eye on your competition, bring a gift: Animals have some practical advice for finding a mate.
-
 Climate
ClimateDesert songbirds increasingly at risk of dehydration
With no efforts to curb climate warming, hot spots in the U.S. Southwest could turn uninhabitable for some songbirds.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsCoral reef crab named after Harry Potter characters
Bizarre rubble-dwelling crab named after critter collector and Harry Potter characters.
-
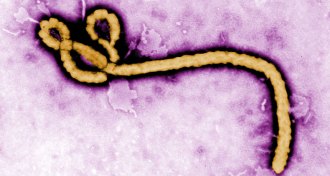 Life
LifeRapid Ebola test to detect early infection in the works
Scientists are developing highly specific antibodies to detect Ebola sooner.
-
 Oceans
OceansFleeting dead zones can muck with seafloor life for decades
Low-oxygen conditions can fundamentally disrupt seafloor ecosystems and increase carbon burial, new research shows.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRicin poisoning may one day be treatable with new antidote
Mice treated with a blend of antibodies survived even when treated days after exposure to ricin.
By Meghan Rosen