Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFrog slime protein fights off the flu
Urumin, a protein found in Indian frog mucus secretions, has a knack for taking down H1 flu viruses, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFrog slime protein fights off the flu
Urumin, a protein found in Indian frog mucus secretions, has a knack for taking down H1 flu viruses, a new study finds.
-
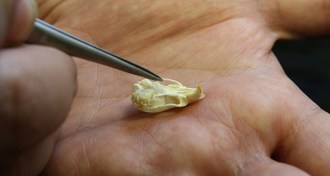 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHow the house mouse tamed itself
When people began to settle down, animals followed. Some made successful auditions as our domesticated species. Others — like mice — became our vermin, a new study shows.
-
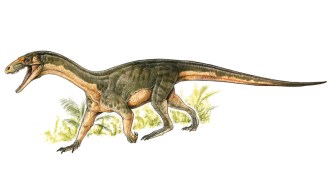 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly dinosaur relative sported odd mix of bird, crocodile-like traits
Teleocrater rhadinus gives researchers a better picture of what early dinosaur relatives looked like.
-
 Animals
AnimalsImprobable ‘black swan’ events can devastate animal populations
Conservation managers should take a note from the world of investments and pay attention to “black swan” events, a new study posits.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHawk moths convert nectar into antioxidants
Hawk moths use their sugary diet to make antioxidants that protect their muscles.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSize matters to lizards, but numbers may not
Scientists have sized up the quantitative abilities of lizards and found that reptiles may not be as good with numbers as other vertebrates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYoung eels use magnetic ‘sixth sense’ to navigate
Migrating eels use Earth’s magnetic field.
-

-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsVolcanic eruptions nearly snuffed out Gentoo penguin colony
Penguin poop dumps data on how a Gentoo colony responded to ancient volcanic eruptions.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsVolcanic eruptions nearly snuffed out Gentoo penguin colony
Penguin poop dumps data on how a Gentoo colony responded to ancient volcanic eruptions.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene knockouts in people provide drug safety, effectiveness clues
People naturally lacking certain genes give clues about drug safety and efficacy, a study in Pakistanis shows.