Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSpecialized protein helps these ground squirrels resist the cold
A less active cold-sensing protein explains, in part, why some hibernating ground squirrels are more tolerant of chilly conditions than the animals’ nonhibernating kin.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn marine mammals’ battle of the sexes, vaginal folds can make the difference
Patricia Brennan and colleagues found certain female ocean mammals have vaginal folds that give them an advantage in mating
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEven brain images can be biased
Brain scan studies that are drawn from rich and well-educated groups could lead to biased ideas of how our brains develop.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIn a tally of nerve cells in the outer wrinkles of the brain, a dog wins
Among some carnivores, golden retrievers rate at the top for numbers of nerve cells, study finds.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThese are the most-read Science News stories of 2017
From Cassini and eclipses to ladybugs and dolphins, Science News online readers had a wide variety of favorite stories on our website.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society2017 delivered humility, and proved our potential
Acting Editor in Chief Elizabeth Quill reflects on some of the top scientific stories of 2017.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCRISPR gene editing moved into new territory in 2017
Scientists edited viable human embryos with CRISPR/Cas9 this year.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe Larsen C ice shelf break has sparked groundbreaking research
The hubbub over the iceberg that broke off Larsen C may have died down, but scientists are just getting warmed up to study the aftermath.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineApproval of gene therapies for two blood cancers led to an ‘explosion of interest’ in 2017
The first gene therapies approved in the United States are treating patients with certain types of leukemia and lymphoma.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains of former football players showed how common traumatic brain injuries might be
Examinations of NFL players’ postmortem brains turned up chronic traumatic encephalopathy in 99 percent of samples in large dataset.
-
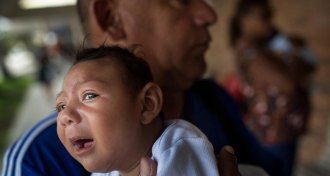 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika cases are down, but researchers prepare for the virus’s return
The number of Zika cases in the Western Hemisphere have dropped this year, but the need for basic scientific and public health research of the virus remains strong.
-
 Animals
AnimalsTicks had a taste for dinosaur blood
A tick found trapped in amber is evidence the bloodsuckers preyed on feathered dinosaurs, a new study says.