Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsPollution regulations help Chesapeake Bay seagrass rebound
Regulations that have reduced nitrogen runoff into the Chesapeake Bay are driving the recovery of underwater vegetation.
-
 Earth
EarthBy 2100, damaged corals may let waves twice as tall as today’s reach coasts
Structurally complex coral reefs can defend coasts against waves, even as sea levels rise.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPenguin supercolony discovered in Antarctica
Scientists have found a penguin supercolony living on tiny, remote Antarctic islands.
By Katy Daigle -
 Earth
EarthEarly land plants led to the rise of mud
New research suggests early land plants called bryophytes, which include modern mosses, helped shape Earth’s surface by creating clay-rich river deposits.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIt’s official: Termites are just cockroaches with a fancy social life
On their latest master list of arthropods, U.S. entomologists have finally declared termites to be a kind of cockroach.
By Susan Milius -
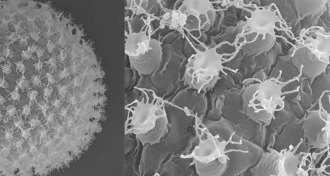 Animals
AnimalsA new species of tardigrade lays eggs covered with doodads and streamers
These elegant eggs hint that a tardigrade found in a Japanese parking lot is a new species.
By Susan Milius -
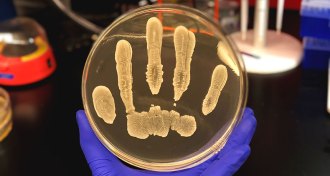 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman skin bacteria have cancer-fighting powers
Strains of a bacteria that live on human skin make a compound that suppressed tumor growth in mice.
-
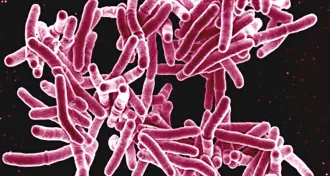 Microbes
MicrobesA new way to make bacteria glow could simplify TB screening
A new dye to stain tuberculosis bacteria in coughed-up mucus and saliva could expedite TB diagnoses and drug-resistance tests.
-
 Life
LifeA rare rainstorm wakes undead microbes in Chile’s Atacama Desert
Microbial life in Chile’s Atacama Desert bursts into bloom when moisture is available.
-
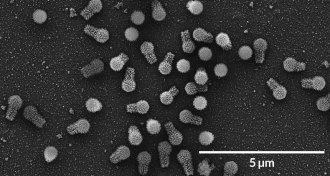 Life
LifeThese giant viruses have more protein-making gear than any known virus
Scientists have found two more giant viruses in extreme environments in Brazil.
By Dan Garisto -
 Animals
AnimalsThis scratchy hiss is the closest thing yet to caterpillar vocalization
A new way that caterpillars make noise may involve (tiny) teakettle‒style turbulence.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSome flu strains can make mice forgetful
Mice infected with influenza had memory problems a month later, a result that hints at a link between infections and brain performance.