Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA caterpillar outwits corn defenses by gorging on fattening ‘junk’ food
The crop plants defend themselves with zombie-maker wasps, but one pest has a desperate work-around.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthKeeping global warming to 1.5 degrees C helps most species hold their ground
Holding global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2100 could help protect tens of thousands of insect, plant and vertebrate species.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient Chinese farmers sowed literal seeds of change in Southeast Asia
Two waves of ancient migration from China to Southeast Asia spread farming and languages.
By Bruce Bower -
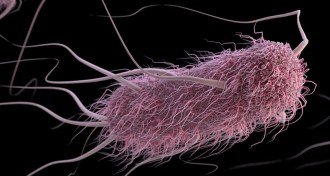 Life
LifeYour blood type might make you more likely to get traveler’s diarrhea
People with type A blood are more likely to develop severe diarrhea from E. coli infections.
-
 Animals
Animals50 years ago, scientists warned of a sparrow’s extinction
Only 17 dusky seaside sparrows remained in 1968. Today, there are none.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGreen blood in lizards probably evolved four times
Pigment buildups that would cause jaundice in people are normal for some New Guinea skinks.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsMeet the speedsters of the plant world
Researchers have recently uncovered a diverse array of mechanisms that allow plants to move — often faster than the blink of an eye.
By Dan Garisto -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWe’ve got the genes for science journalism
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses how genetic testing might not be reliable enough for people to plan for the future.
By Nancy Shute -
 Animals
AnimalsReaders amazed by Jupiter discoveries, giant viruses and more
Readers had questions about the latest findings of Jupiter, giant viruses being recognized as a new kingdom of life and tardigrade poop.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHere’s how hefty dinosaurs sat on their eggs without crushing them
Some heavier dinos had a strategy to keep eggs warm without crushing them: sit in an opening in the middle of the clutch instead of on top of them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a deep-sea geology trip led researchers to a doomed octopus nursery
A healthy population of cephalopods could be hiding nearby, though, a new study contends.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWith a little convincing, rats can detect tuberculosis
TB-sniffing rats prove more accurate in detecting infection, especially in children, than the most commonly used diagnostic tool.
By Yao-Hua Law