Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBees join an exclusive crew of animals that get the concept of zero
Honeybees can pass a test of ranking ‘nothing’ as less than one.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsWhy using genetic genealogy to solve crimes could pose problems
Rules governing how police can use DNA searches in genealogy databases aren’t clear, raising civil rights and privacy concerns.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn a conservation catch-22, efforts to save quolls might endanger them
After 13 generations isolated from predators, the endangered northern quoll lost its fear of them.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAt-home telomere testing is not a reliable marker of aging, researcher says
Telomere testing for consumers offers a poor measure of “biological age,” says Johns Hopkins oncologist Mary Armanios.
-
 Life
LifeDogs carry a surprising variety of flu viruses
Dogs in China carry a wider variety of flu viruses than previously thought, and may be capable of passing the flu to humans.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat we know — and don’t know — about a new migraine drug
A migraine prevention drug was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. But some questions about the therapy remain.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsPrivacy and consumer genetic testing don’t always mix
Interested in taking a direct-to-consumer genetic test? Here are some things you should know.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Outbreak’ puts the life cycle of an epidemic on display
At the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, the exhibit “Outbreak” highlights how infectious diseases shape our world.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhat consumer DNA data can and can’t tell you about your risk for certain diseases
Consumers face lots of choices and unanswered questions when they get personal genomic information related to disease risk from the Internet.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHere’s why scientists are questioning whether ‘sonic attacks’ are real
Sonic attacks would be hard to pull off and a terrible way of incapacitating diplomats, experts say.
-
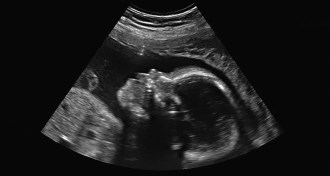 Genetics
GeneticsGuidelines call for limits to whole genome testing for fetuses
Powerful tests offer unprecedented detail about fetal genomes. But whole-genome tests aren’t ready for widespread use yet, doctors caution.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTreating roads with oil and gas wastewater may spread harmful pollution
When spread on roads, wastewater from oil and gas production can leach radium and other contaminants into the environment, a new study finds.