Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists successfully transplant lab-grown lungs into pigs
Pigs implanted with lab-grown lungs recovered from surgery with no breathing problems.
-
 Health & Medicine
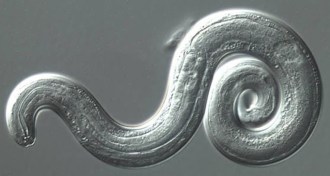
Health & MedicineRat lungworm disease is popping up in the mainland United States
A disease caused by a parasite endemic to Asia sickened at least 12 people in eight states in the continental United States from 2011 to 2017.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe ‘language gene’ didn’t give humans a big leg up in evolution
Scientists have long debated the role of a gene called FOXP2 in recent human evolution.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsIndonesia’s pygmies didn’t descend from hobbits, DNA analysis suggests
Short people living on the Indonesian island of Flores don’t appear to have DNA from controversial, small-bodied Stone Age hominids called hobbits.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil teeth show how a mass extinction scrambled shark evolution
The dinosaur-destroying mass extinction event didn’t wipe out sharks, but it did change their fate.
-
 Health & Medicine
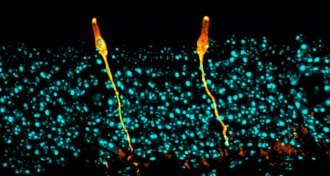
Health & MedicineNewfound airway cells may breathe life into tackling cystic fibrosis
A newly discovered cell in the lining of the airways is the primary site of activity for the gene that, when defective, causes cystic fibrosis.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWith one island’s losses, the king penguin species shrinks by a third
Once home to the largest known colony of king penguins, Île aux Cochons has lost most of its birds for unknown reason.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSoccer headers may hurt women’s brains more than men’s
Women sustain more damage from heading soccer balls than men, a brain scan study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA medical mystery reveals a new host for the rat lungworm parasite
Doctors report that A. cantonensis was transmitted to two people who ate raw centipedes, but you can get it from other creatures as well.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAnxiety in monkeys is linked to hereditary brain traits
A key brain connection may be behind childhood anxiety, brain scans of monkeys suggest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis tick may play a part in gumming up your arteries
Having antibodies to a sugar tied to red-meat allergy is associated with more plaque in the artery walls, a small study shows.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesHow a slime mold near death packs bacteria to feed the next generation
Social amoebas that farm bacteria for food use proteins to preserve the crop for their offspring.
By Susan Milius