Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
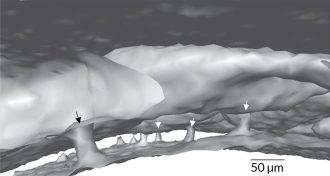 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNewfound skull tunnels may speed immune cells’ trek to brain injuries
Minuscule channels connect the skull to the brain’s outer membrane, studies in mice and people show.
-
 Life
LifeHow the poppy got its pain-relieving powers
Analyzing the poppy’s genome reveals the evolutionary history of morphine.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCRISPR gene editing relieves muscular dystrophy symptoms in dogs
Scientists have used CRISPR’s molecular scissors in beagle puppies to repair a genetic mutation that causes muscular dystrophy.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNaked mole-rats eat the poop of their queen for parenting cues
Hormones in the naked mole-rat queen’s poop turn subordinate nest-mates into surrogate parents.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThere’s method in a firefly’s flashes
Fireflies use their flashing lights for mating and maybe even to ward away predators.
-
 Life
LifeWe may now know when hand, foot and mouth disease outbreaks will occur
Birthrates and immunity rates predict the spread of viruses that cause hand, foot and mouth disease.
-
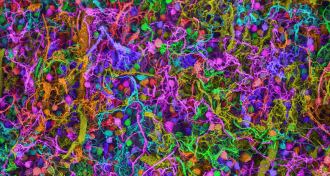 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow antibodies attack the brain and muddle memory
Human antibodies that target key brain proteins cause memory trouble when delivered into mice’s brains.
-
 Humans
HumansMeet the first known child of a Neandertal and a Denisovan
DNA analysis of a bone fragment reveals Neandertal movements between Siberia and western Europe.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA fossil mistaken for a bat may shake up lemurs’ evolutionary history
On Madagascar, a type of lemur called aye-ayes may have a singular evolutionary history.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsAmericans support genetically engineering animals for people’s health
Genetically engineering animals is OK with Americans if it improves human health, a new poll reveals.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsA freshwater, saltwater tug-of-war is eating away at the Everglades
Saltwater is winning in the Everglades as sea levels rise and years of redirecting freshwater flow to support agriculture and population growth
-
 Life
LifeHow salamanders can regrow nearly complete tails but lizards can’t
Differences in stem cells in the spinal cord explain the amphibians’ ability.