Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeExplore the history of blood from vampires to the ‘Menstrual Man’
Rose George’s book ‘Nine Pints’ offers readers an engaging and insightful cultural and scientific history of blood.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn cadaver caves, baby beetles grow better with parental goo
A dead mouse — with the right microbial treatment from beetle parents — becomes a much better nursery than your average carcass.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsHow nectar bats fly nowhere
Exquisitely sensitive tech makes first direct measurements of the forces of bat wingbeats.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsGenealogy databases could reveal the identity of most Americans
Keeping your DNA private is getting harder.
-
 Tech
TechSelf-driving cars see better with cameras that mimic mantis shrimp vision
A new type of camera that sees in polarized light across a wide range of light intensities could help make self-driving cars safer on the road.
-
 Life
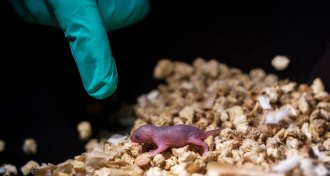
LifeGene editing creates mice with two biological dads for the first time
Scientists have used CRISPR/Cas9 to make mice with two biological fathers.
-
 Life
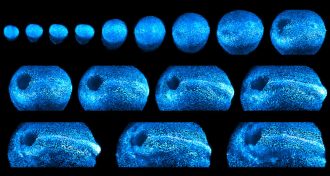
LifeSee these dazzling images of a growing mouse embryo
A new microscope creates intimate home movies of mice embryos taking shape, and could shed light on the mysterious process of mammalian development.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhat bees did during the Great American Eclipse
A rare study of bees during a total solar eclipse finds that the insects buzzed around as usual — until totality.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
Plants50 years ago, a 550-year-old seed sprouted
Old seeds can sprout new plants even after centuries of dormancy.
-
 Earth
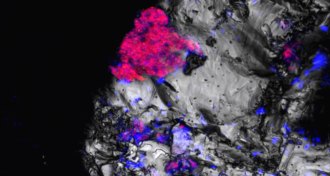
EarthThese light-loving bacteria may survive surprisingly deep underground
Traces of cyanobacteria DNA suggest that the microbes live deep below Earth’s surface.
-
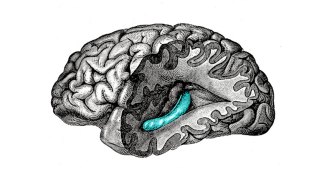 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow your brain is like a film editor
A brain structure called the hippocampus may slice our continuous existence into discrete chunks that can be stored as memories.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistrySpeeding up evolution to create useful proteins wins the chemistry Nobel
The three winners, which include the fifth woman to win the chemistry prize, pioneered techniques used to fashion customized proteins for new biofuels and drugs.
By Laurel Hamers and Maria Temming