Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Physics
PhysicsReaders inquire about a Neptune-sized moon, nuclear pasta and more
Readers had questions about a Neptune-sized moon, nuclear pasta and the search for extraterrestrial life.
-
 Animals
AnimalsRebel honeybee workers lay eggs when their queen is away
A honeybee queen’s absence in the colony triggers some workers to turn queen-like and lay eggs, sometimes in other colonies.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Life
LifeHow some sap-sucking insects fling their pee
Sharpshooters hurl their pee with structure called a stylus, which sends droplets flying at 20 times the acceleration of Earth’s gravity.
-
 Life
LifeThese new tweezers let scientists do biopsies on living cells
Nanotweezers that can pluck molecules from cells without killing them could enable real-time analysis of the insides of healthy and diseased cells.
-
 Life
LifeDads, not just moms, can pass along mitochondrial DNA
Data from three families suggest that in rare cases children can inherit mitochondria from their fathers.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentAn acid found in soil may make a disease killing deer less infectious
An incurable neurodegenerative disease crippling North American deer, elk and moose may be thwarted by an organic soil compound.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA jumping spider mom nurses her brood for weeks on milk
Even after spiderlings start hunting for themselves, they come to mom for milk.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceZaps to a certain spot in the brain may ease depression
When implanted electrodes stimulated a brain region just behind the eyes, people’s spirits were raised immediately.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe researcher who created CRISPR twins defends his work but fails to quell controversy
After getting a glimpse of data behind the birth of the first gene-edited babies, many scientists question the study’s ethics and medical necessity.
-
 Health & Medicine
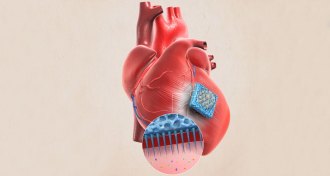
Health & MedicineA patch studded with tiny needles may help heart attack survivors recover
A bandage that sticks to the surface of the heart exudes proteins and other molecules that help muscle cells grow.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsBeavers are engineering a new Alaskan tundra
Climate change has enabled the recent expansion of beavers into northwestern Alaska, a trend that could have major ecological consequences for the region in the coming decades.
By Sid Perkins -
 Genetics
GeneticsChinese scientists raise ethical questions with first gene-edited babies
Scientists say gene editing of human embryos isn’t yet safe, and creating babies was unethical.