Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDNA tests of Lassa virus mid-outbreak helped Nigeria target its response
New technology for analyzing genetic data quickly in the field guided how Nigeria dealt with an outbreak of Lassa fever in 2018.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureA new way to genetically tweak photosynthesis boosts plant growth
A new chemical road map for a process called photorespiration in plant cells could reduce energy waste to increase plant productivity.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPoop provides a link in determining penguin diet from space
Scientists have figured out what foods dominate an Adélie penguin colony’s diet by looking at Landsat imagery. But to do so, they had to start with penguin guano.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMacaques take turns while chattering
Japanese monkeys take turns while communicating. Adjusting response times while chattering, macaques intentionally pause like humans do when chatting.
By Katie Brown -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThese are the most-read Science News stories of 2018
From male birth control to wombat poop, Science News online readers had a wide variety of favorite stories on our website.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThese 2018 findings could be big news — if they turn out to be true
Discoveries about fossils, the Big Bang and more could shake up the scientific world – if they turn out to be true.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPterosaurs may have been covered in fur and primitive feathers
A new study provides evidence of plumelike structures in ancient flying reptiles.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyMore plants survived the world’s greatest mass extinction than thought
Fossil plants from Jordan reveal more plant lineages that made it through the Great Dying roughly 252 million years ago.
-
 Neuroscience
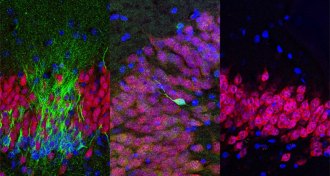
NeuroscienceThe battle over new nerve cells in adult brains intensifies
It’s not yet time to abandon the idea that adult human brains make new nerve cells.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive asexual midges may upset Antarctica’s delicate moss banks
Fast-multiplying insects with earthworm powers have invaded Antarctica, and scientists are worried about how their waste could affect the continent.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
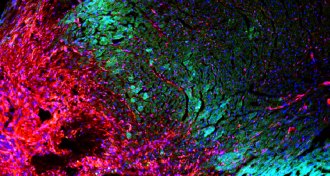
LifeMice lack stem cells in the heart needed for self-repair
Adult mice hearts have no stem cells, a study finds. The same may be true for people, and that’s not welcome news for those who’ve had a heart attack.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTumor ‘organoids’ may speed cancer treatment
Growing mini tumors in a lab dish, researchers can screen compounds to find promising combinations for treating rare cancers.