Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEpileptic seizures may scramble memories during sleep
Overnight seizures seemed to muddle memories in people with epilepsy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA single sweaty workout may boost some people’s memory
Memory improvements after a short bout of exercise mirrored those seen after months of training.
-
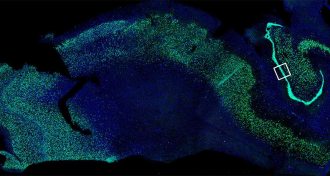 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSigns of new nerve cells spotted in adult brains
A study finds new evidence that adult brains grow new nerve cells, even the brain of an octogenarian.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologySaber-toothed cats were fierce and family-oriented
New details shift the debate on whether Smilodon lived and hunted in packs, and answer questions about other behaviors and abilities.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWomen have a new weapon against postpartum depression, but it’s costly
The newly approved drug brexanolone simulates a natural hormone to alleviate symptoms of postpartum depression.
By Jeremy Rehm -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNewfound fossils in China highlight a dizzying diversity of Cambrian life
A new treasure trove of Cambrian fossils in China dating to 518 million years ago could rival Canada’s Burgess Shale.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new ketamine-based antidepressant raises hope — and questions
Little is known about the long-term effects on people of a newly approved antidepressant based on the anesthetic ketamine.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyIn a first, a fossilized egg is found preserved inside an ancient bird
Scientists have found the first known fossil of a bird that died with an unlaid egg inside its body. The egg has been crushed by pressure over time.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a tiger transforms into a man-eater
‘No Beast So Fierce’ examines the historical and environmental factors that turned a tiger in Nepal and India into a human-killer.
-
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePeople can sense Earth’s magnetic field, brain waves suggest
An analysis of brain waves offers new evidence that people subconsciously process information about the planet’s magnetism.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMeet India’s starry dwarf frog — a species with no close relatives
The newly identified starry dwarf frog represents a new species, genus and potentially even a new family.
By Jeremy Rehm -
 Genetics
GeneticsResurrecting woolly mammoth cells is hard to do
Japanese scientists say some proteins in frozen mammoth cells may still work after 28,000 years. But that activity may be more mouse than mammoth.