Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA scientist used chalk in a box to show that bats use sunsets to migrate
A new device for investigating bat migration suggests that the flying mammals orient themselves by the setting sun.
By Yao-Hua Law -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe herbal supplement kratom comes with risks
The supplement kratom can cause heart racing and agitation.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA genetic scorecard could predict your risk of being obese
A genetic score predicts who is at risk of severe obesity, but experts say lifestyle matters more than genes.
-
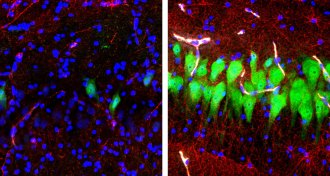 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDead pig brains bathed in artificial fluid showed signs of cellular life
Four hours after pigs died, the animals’ brain cell activity was restored by a sophisticated artificial system.
-
 Animals
AnimalsParenting chores cut into how much these bird dads fool around
Frantic parenting demands after eggs hatch curtail male black coucals’ philandering excursions the most, a study finds.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsSome people may have genes that hamper a drug’s HIV protection
Newly discovered genetic variants could explain why an anti-HIV medication doesn’t protect everyone.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHow chemical exposure early in life is ‘like a ticking time bomb’
Some early life experiences can affect health, but only if unmasked by events in adulthood.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNASA’s Twins Study reveals effects of space on Scott Kelly’s health
Ten research groups studying the twin astronauts found long-term spaceflight can alter a person’s physiology and gene activity.
By Jeremy Rehm -
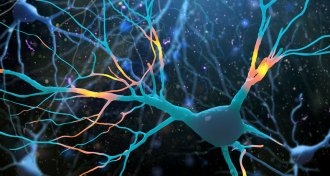 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineKetamine cultivates new nerve cell connections in mice
In mice, ketamine prods nerve cells to connect, which may explain the hallucinogenic drug’s ability to ease depression.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change made the Arctic greener. Now parts of it are turning brown.
Arctic browning could have far-reaching consequences for people and wildlife, affecting habitat and atmospheric carbon uptake as well as increasing wildfire risk.
By Hannah Hoag -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceOur brains sculpt each other. So why do we study them in isolation?
Studying individual brains may not be the way to figure out the human mind, a social neuroscientist argues.
-
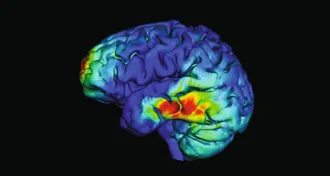 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen an older person’s brain waves are in sync, memory is boosted
A brain stimulation treatment that nudges older people’s brain waves into sync could lead to noninvasive therapies for dementia and other disorders.