Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentChemicals in biodegradable food containers can leach into compost
PFAS compounds from compostable food containers could end being absorbed by plants and later eaten by people, though the health effects are unclear.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe Smithsonian’s ‘Deep Time’ exhibit gives dinosaurs new life
The Smithsonian’s renovated fossil hall puts ancient dinosaurs and other creatures in context.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHow one fern hoards toxic arsenic in its fronds and doesn’t die
To survive high levels of arsenic, a fern sequesters the heavy metal in its shoots with the help of three proteins.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceA new experiment didn’t find signs of dreaming in brain waves
Brain activity that powers dreams may reveal crucial insight into consciousness, but a new study failed to spot evidence of the neural flickers.
-
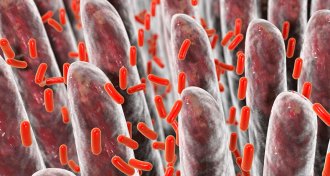 Life
LifeGut bacteria may change the way many drugs work in the body
A new survey of interactions between microbes and medications suggests that gut bacteria play a crucial role in how the body processes drugs.
-
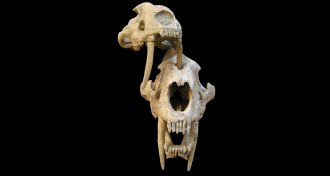 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossils reveal saber-toothed cats may have pierced rivals’ skulls
Two Smilodon fossil skulls from Argentina have puncture holes likely left by the teeth of rival cats.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA fungus weaponized with a spider toxin can kill malaria mosquitoes
In controlled field experiments in Burkina Faso, a genetically engineered fungus reduced numbers of insecticide-resistant mosquitoes that can carry malaria.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAfrica’s first herders spread pastoralism by mating with foragers
DNA unveils long-ago hookups between early pastoralists and native hunter-gatherers in Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyQuestions about solar storms, slingshot spiders and more reader feedback
Readers had questions about solar storms, a robotic gripper, slingshot spiders and more.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResurgence of measles is a tale as old as human history
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute discusses the recent global measles outbreak and the history of the spread of pathogens.
By Nancy Shute -
 Animals
AnimalsA 50-million-year-old fossil captures a swimming school of fish
Analysis of a fossilized fish shoal suggests that animals may have evolved coordinated group movement around 50 million years ago.
-
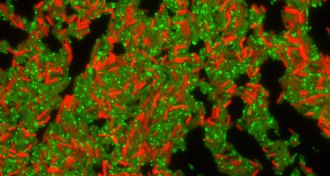 Life
LifeHow bacteria nearly killed by antibiotics can recover — and gain resistance
A pump protein can keep bacteria alive long enough for the microbes to develop antibiotic resistance.