Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
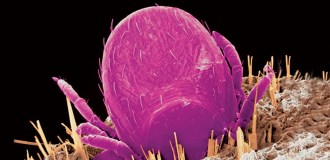
Health & MedicineNew approaches may help solve the Lyme disease diagnosis dilemma
Lyme disease is hard to detect, but scientists are investigating new diagnostic approaches.
By Laura Beil -
 Animals
AnimalsParasites ruin some finches’ songs by chewing through the birds’ beaks
Parasitic fly larvae damage the beaks of Galápagos finches, changing their mating songs and possibly causing females to pick males of a different species.
-
 Animals
AnimalsU.S. honeybees had the worst winter die-off in more than a decade
Colonies suffered from parasitic, disease-spreading Varroa mites. Floods and fire didn’t help.
By Susan Milius -
 Oceans
OceansThe world’s fisheries are incredibly intertwined, thanks to baby fish
A computer simulation reveals how one nation's management of its fish spawning grounds could significantly help or hurt another country's catch.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMice and bats’ brains sync up as they interact with their own kind
The brain activity of mice and bats aligns in social settings, a coordination that may hold clues about how social context influences behavior.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA confirms a weird Greenland whale was a narwhal-beluga hybrid
DNA analysis of a skull indicates that the animal had a narwhal mother and beluga father.
-
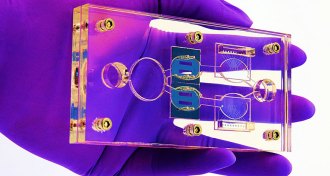 Life
LifeThis body-on-a-chip mimics how organs and cancer cells react to drugs
The multiorgan system could help test new and existing drugs for effectiveness and unwanted side effects.
-
 Life
Life‘Sneezing’ plants may spread pathogens to their neighbors
A “surface tension catapult” can fling dewdrops carrying fungal spores from water-repellent leaves.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFemale rats face sex bias too
In neurobiological studies, male lab animals tend to outnumber females, which are considered too hormonal. Scientists say it’s time for that myth to go.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHyenas roamed the Arctic during the last ice age
Two teeth confirm the idea that hyenas crossed the Bering land bridge into North America, a study finds.
-
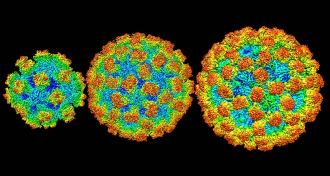 Life
LifeNorovirus close-ups might help fight stomach flu
Detailed views of a common stomach virus that causes vomiting and diarrhea could aid vaccine and disinfectant development.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyReaders boggled by black hole behemoth
Readers had questions about the first image of a black hole and a chytrid fungus.