Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
Life50 years ago, scientists thought they knew why geckos had sticky feet
50 years ago, scientists thought gecko feet had suction cups that allowed the animals to stick to surfaces. Today we know tiny hairs do the job.
By Kyle Plantz -
 Life
LifeFecal transplants might help make koalas less picky eaters
Poop-transplant pills changed the microbial makeup of koalas’ guts. That could allow the animals to adapt when a favorite type of eucalyptus runs low.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHoneybee brain upgrades may help the insects find food
Changes in honeybee neurons may help the insects decode their fellow foragers’ waggle dances.
-
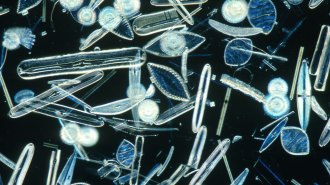 Earth
EarthOcean acidification could weaken diatoms’ glass houses
Ocean acidification may lead to smaller, lighter diatoms in seawater, which could also shrink how much carbon the tiny ocean algae can help sequester.
-
 Life
LifeHow a newly identified bacterium saps corals of their energy
A parasitic bacterium that preys on corals quickly reproduces when it senses more nutrients in its host.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow strep throat may spark OCD and anxiety in some kids
A potential link between strep throat and sudden mental disorders in children raises questions about how infections can alter the brain.
-
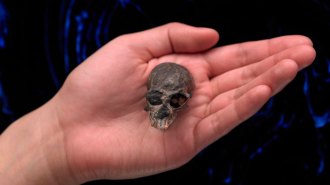 Anthropology
AnthropologyA tiny skull fossil suggests primate brain areas evolved separately
Digital reconstruction of a fossilized primate skull reveals that odor and vision areas developed independently starting 20 million years ago or more.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhat human and mouse brains do and don’t have in common
A large comparison of human and mouse brain cells highlights key differences that could have implications for research on depression or Alzheimer’s.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy one biologist chases hurricanes to study spider evolution
For more rigorous spider data, Jonathan Pruitt rushes into the paths of hurricanes.
By Susan Milius -
 Humans
HumansIndia’s Skeleton Lake contains the bones of mysterious European migrants
Not all of the hundreds of skeletons found at a north Indian lake are from the same place or period. What killed any of these people is still unknown.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeBig and bold wasp queens may create more successful colonies
A paper wasp queen’s personality and body size could help predict whether the nest she has founded will thrive.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceImaging scans show where symbols turn to letters in the brain
Scientists watched brain activity in a region where reading takes root, and saw a hierarchy of areas that give symbols both sound and meaning.