Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeWe’ve lost 3 billion birds since 1970 in North America
Scientists estimated the change in total number of individual birds since 1970. They found profound losses spread among rare and common birds alike.
-
 Humans
HumansAncient DNA reveals the first glimpse of what a Denisovan may have looked like
A controversial technique reconstructs a teenage Denisovan’s physical appearance from genetics.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeClimate change may be throwing coral sex out of sync
Several widespread corals in the Red Sea are flubbing cues to spawn en masse.
By Susan Milius -
 Agriculture
AgricultureBirds fed a common pesticide lost weight rapidly and had migration delays
Scientists have previously implicated neonicotinoid pesticides in declining bee populations. Now a study suggests that songbirds are affected, too.
By Maanvi Singh -
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, polio was still circulating in the United States
The world has never been closer to eradicating polio, but the disease could come roaring back where vaccination is spotty.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘The Nature of Life and Death’ spotlights pollen’s role in solving crimes
In ‘The Nature of Life and Death,’ botanist Patricia Wiltshire recounts some of her most memorable cases.
By Sid Perkins -
 Humans
HumansArtists who paint with their feet have ‘toe maps’ in their brains
Brain specialization comes with toe specialization in people who use their feet for painting, eating and writing.
-
 Humans
HumansDNA indicates how ancient migrations shaped South Asian languages and farming
Farming in the region may have sprung up locally, while herders from afar sparked language changes.
By Bruce Bower -
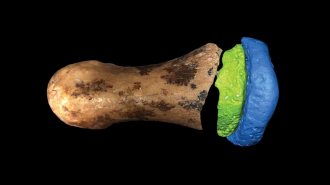 Anthropology
AnthropologyThis ancient Denisovan finger bone is surprisingly humanlike
Despite Neandertal ties, extinct hominids called Denisovans had a touching link to humans, a new study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeHuman meddling has manipulated the shapes of different dog breeds’ brains
By analyzing the shape of different dog breeds’ brains, researchers show how humans have manipulated the animals’ brain anatomy.
-
 Life
LifeFly fossils might challenge the idea of ancient trilobites’ crystal eyes
Fossilized crane flies from 54 million years ago probably got their crystal lenses after death.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsThere’s no evidence that a single ‘gay gene’ exists
Many genetic factors with small effects combine with one’s environment to influence sexual behavior, researchers say.